Dopamine is released in the striatum during human emotional processing
- PMID: 21057339
- PMCID: PMC2997433
- DOI: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e3283410955
Dopamine is released in the striatum during human emotional processing
Abstract
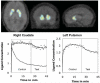
As the role of dopamine in human emotional processing is unclear, we used a dynamic molecular imaging technique to examine whether striatal dopamine is released during processing of negative emotions in healthy volunteers. After volunteers have received an intravenous injection of a dopamine receptor ligand C-raclopride, they were asked to perform a task that elicited negative emotions. During task performance the ligand concentration was measured dynamically using a positron emission tomography camera. Analysis of the data indicated that the task performance is associated with dopamine release in the head of caudate and in the dorsal putamen bilaterally.
Figures
References
-
- Damasio AR, Grabowski TJ, Bechara A, Damasio H, Ponto LL, Parvizi J, et al. Subcortical and cortical brain activity during the feeling of self-generated emotions. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:1049–1056. - PubMed
-
- Hamann S, Mao H. Positive and negative emotional verbal stimuli elicit activity in the left amygdala. Neuroreport. 2002;13:15–19. - PubMed
-
- Haralambous T, Westbrook RF. An infusion of bupivacaine into the nucleus accumbens disrupts the acquisition but not the expression of contextual fear conditioning. Behav Neurosci. 1999;113:925–940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

