Real-time free cortisol quantification among critically ill children
- PMID: 21057361
- PMCID: PMC3566572
- DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181fe4474
Real-time free cortisol quantification among critically ill children
Abstract
Objectives: Ascertainment of adrenal function assessing free rather that total cortisol may be beneficial for the diagnosis of critical illness-related cortisol insufficiency. We hypothesized that centrifugal ultrafiltration would provide timely free cortisol data that highly correlated with the gold standard, but logistically cumbersome, equilibrium dialysis technique when the free cortisol fractions were identically quantified by chemiluminescence immunoassay. We also hypothesized that free cortisol would correlate with illness severity in a large cohort of critically ill children.
Design: Prospective, multi-institutional, observational cohort investigation.
Setting: Seven pediatric intensive care units within the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Collaborative Pediatric Critical Care Research Network.
Patients: One hundred sixty-five critically ill children across the spectrum of illness severity.
Interventions: Blood sampling.
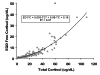
Measurements and main results: Time to derive plasma free cortisol concentrations after centrifugal ultrafiltration or equilibrium dialysis fractionation with chemiluminescence immunoassay was approximately 2 vs. approximately 24 hrs, respectively. Using centrifugal ultrafiltration, mean plasma free cortisol was 4.1 ± 6.7 μg/dL (median, 1.6 μg/dL; range, 0.2-43.6 μg/L), representing an average of 15.2 ± 9.4% of total cortisol. Nearly 60% of subjects exhibited free cortisol <2 and 30% <0.8 μg/dL, previously suggested threshold concentrations for defining critical illness-related cortisol insufficiency. Plasma-free cortisol concentrations comparing centrifugal ultrafiltration vs. equilibrium dialysis fractionation demonstrated a strong correlation (R2 = 0.97). For free cortisol <2 μg/dL, Bland-Altman analysis revealed minimal negative bias for the centrifugal ultrafiltration technique. Illness severity assessed by Pediatric Risk of Mortality III correlated moderately with free cortisol and percent total cortisol as free cortisol.
Conclusions: Determination of centrifugal ultrafiltration fractionated free cortisol was fast and results correlated highly with equilibrium dialysis fractionated free cortisol. Many children exhibited free cortisol <2 and <0.8 μg/dL but did not demonstrate clinical evidence of critical illness-related cortisol insufficiency. This study ascertains that real-time free cortisol quantification is feasible to potentially help guide clinical decision-making for cortisol replacement therapy in the pediatric intensive care unit.
Figures







References
-
- Webster JI, Tonelli L, Sternberg EM. Neuroendocrine regulation of immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:125–163. - PubMed
-
- Chrousos GP. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1995;332(20):1351–1362. - PubMed
-
- Marik PE. Critical illness-related corticosteroid insufficiency. Chest. 2009;135(1):181–193. - PubMed
-
- Venkatesh B, Cohen J, Hickman I, et al. Evidence of altered cortisol metabolism in critically ill patients: a prospective study. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33(10):1746–1753. - PubMed
-
- Dimopoulou I, Alevizopoulou P, Dafni U, et al. Pituitary-adrenal responses to human corticotropin-releasing hormone in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med. 2007;33(3):454–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U10HD049945/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01HD049934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD050012/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD049945/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD049981/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD050096/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD049981/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD050096/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD049983/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025014/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 HD107773/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD050096/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD049983/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD050012/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HD049934/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10HD500009/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

