Shortening of alkaline DNA unwinding time does not interfere with detecting DNA damage to mouse and human spermatozoa in the comet assay
- PMID: 21057514
- PMCID: PMC3739381
- DOI: 10.1038/aja.2010.105
Shortening of alkaline DNA unwinding time does not interfere with detecting DNA damage to mouse and human spermatozoa in the comet assay
Abstract
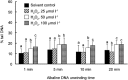
The comet assay was performed on mouse and human spermatozoa to examine the effect of alkaline DNA unwinding time. The spermatozoa were treated in vitro with the DNA-damaging agents, methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) or hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂), and then embedded in agarose gel on glass slides. The slides were immersed in alkaline solution (> pH 13) for 1, 5, 10 and 20 min, and then subjected to the electrophoresis under neutral conditions. In mouse spermatozoa, comet tails seen in solvent controls became brighter and longer as the alkaline DNA unwinding time increased. However, in the MMS-treated mouse spermatozoa, a smaller difference in the damage from that in the solvent control was seen with time within a dose. DNA damage induced by H₂O₂ could also be detected accurately after alkali treatment for 1-20 min. In human spermatozoa, DNA damage induced by MMS and H₂O₂ could be detected in a dose-dependent manner after alkali treatment for 1 min. The ability of the comet assay to detect DNA damage was not adversely affected by the short period (1 min) of the alkaline DNA unwinding time.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effect of safranal, a constituent of Crocus sativus (saffron), on methyl methanesulfonate (MMS)-induced DNA damage in mouse organs: an alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis (comet) assay.DNA Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;26(12):841-6. doi: 10.1089/dna.2007.0631. DNA Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17854266
-
DNA alkylation lesions and their repair in human cells: modification of the comet assay with 3-methyladenine DNA glycosylase (AlkD).Toxicol Lett. 2012 Jan 5;208(1):76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.10.005. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Toxicol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22019460
-
The genetic toxicity of time: importance of DNA-unwinding time to the outcome of single-cell gel electrophoresis assays.Mutat Res. 1997 Apr 29;375(2):125-36. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(97)00008-0. Mutat Res. 1997. PMID: 9202723
-
Genotoxicity of environmental agents assessed by the alkaline comet assay.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005;96 Suppl 1:1-42. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15859009 Review.
-
Technical recommendations to perform the alkaline standard and enzyme-modified comet assay in human biomonitoring studies.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2019 Jul;843:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2019.04.007. Epub 2019 May 1. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2019. PMID: 31421734 Review.
References
-
- Baumgartner A, Cemeli E, Anderson D. The comet assay in male reproductive toxicology. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2009;25:81–98. - PubMed
-
- Angelis KJ, Dusinska M, Collins AR. Single cell gel electrophoresis: detection of DNA damage at different levels of sensitivity. Electrophoresis. 1999;20:2133–8. - PubMed
-
- Koppen G, Angelis KJ. Repair of X-ray induced DNA damage measured by the comet assay in roots of Vicia faba. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1998;32:281–5. - PubMed
-
- Menke M, Chen IP, Angelis KJ, Schubert I. DNA damage and repair in Arabidopsis thaliana as measured by the comet assay after treatment with different classes of genotoxins. Mutat Res. 2001;493:87–93. - PubMed
-
- Codrington AM, Hales BF, Robaire B. Spermiogenic germ cell phase-specific DNA damage following cyclophosphamide exposure. J Androl. 2004;25:354–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

