Correlated conformational events in EF-G and the ribosome regulate translocation
- PMID: 21057527
- PMCID: PMC2997181
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1925
Correlated conformational events in EF-G and the ribosome regulate translocation
Abstract
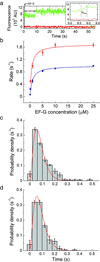
In bacteria, the translocation of tRNA and mRNA with respect to the ribosome is catalyzed by the conserved GTPase elongation factor-G (EF-G). To probe the rate-determining features in this process, we imaged EF-G-catalyzed translocation from two unique structural perspectives using single-molecule fluorescence resonance energy transfer. The data reveal that the rate at which the ribosome spontaneously achieves a transient, 'unlocked' state is closely correlated with the rate at which the tRNA-like domain IV-V element of EF-G engages the A site. After these structural transitions, translocation occurs comparatively fast, suggesting that conformational processes intrinsic to the ribosome determine the rate of translocation. Experiments conducted in the presence of non-hydrolyzable GTP analogs and specific antibiotics further reveal that allosterically linked conformational events in EF-G and the ribosome mediate rapid, directional substrate movement and EF-G release.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Conformational changes of elongation factor G on the ribosome during tRNA translocation.Cell. 2015 Jan 15;160(1-2):219-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.049. Cell. 2015. PMID: 25594181 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated conformational and compositional dynamics drive ribosome translocation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Jun;20(6):718-27. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2567. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23624862 Free PMC article.
-
Role of domains 4 and 5 in elongation factor G functions on the ribosome.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jul 21;300(4):951-61. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3886. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10891280
-
Elongation in translation as a dynamic interaction among the ribosome, tRNA, and elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu.Q Rev Biophys. 2009 Aug;42(3):159-200. doi: 10.1017/S0033583509990060. Q Rev Biophys. 2009. PMID: 20025795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translational elongation factor G: a GTP-driven motor of the ribosome.Essays Biochem. 2000;35:117-29. doi: 10.1042/bse0350117. Essays Biochem. 2000. PMID: 12471894 Review.
Cited by
-
The energy landscape of -1 ribosomal frameshifting.Sci Adv. 2020 Jan 1;6(1):eaax6969. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax6969. eCollection 2020 Jan. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 31911945 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the dynamics of ribosome translocation.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012 Dec;22(6):804-14. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2012.09.004. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 23142574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EF-G catalyzed translocation dynamics in the presence of ribosomal frameshifting stimulatory signals.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Mar 17;45(5):2865-2874. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27799473 Free PMC article.
-
Biological mechanisms, one molecule at a time.Genes Dev. 2011 Jun 15;25(12):1205-31. doi: 10.1101/gad.2050011. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21685361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-amino acids reduce ternary complex stability and alter the translation elongation mechanism.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 27:2024.02.24.581891. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.24.581891. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: ACS Cent Sci. 2024 Jun 04;10(6):1262-1275. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.4c00314. PMID: 38464221 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Wintermeyer W, et al. Mechanisms of elongation on the ribosome: dynamics of a macromolecular machine. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004;32:733–737. - PubMed
-
- Fredrick K, Noller H. Catalysis of ribosomal translocation by sparsomycin. Science. 2003;300:1159–1162. - PubMed
-
- Cukras AR, Southworth DR, Brunelle JL, Culver GM, Green R. Ribosomal proteins S12 and S13 function as control elements for translocation of the mRNA:tRNA complex. Mol Cell. 2003;12:321–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

