MicroRNA-221/222 confers breast cancer fulvestrant resistance by regulating multiple signaling pathways
- PMID: 21057537
- PMCID: PMC3342929
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2010.487
MicroRNA-221/222 confers breast cancer fulvestrant resistance by regulating multiple signaling pathways
Abstract
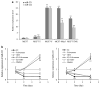
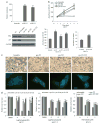
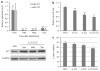
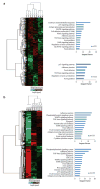
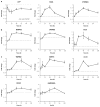
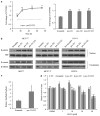
Fulvestrant is a selective estrogen receptor downregulator (SERD) and highly effective antagonist to hormone-sensitive breast cancers following failure of previous tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitor therapies. However, after prolonged fulvestrant therapy, acquired resistance eventually occurs in the majority of breast cancer patients, due to poorly understood mechanisms. To examine a possible role(s) of aberrantly expressed microRNAs (miRNAs) in acquired fulvestrant resistance, we compared antiestrogen-resistant and -sensitive breast cancer cells, revealing the overexpression of miR-221/222 in the SERD-resistant cell lines. Fulvestrant treatment of estradiol (E2)- and fulvestrant-sensitive MCF7 cells resulted in increased expression of endogenous miR-221/222. Ectopic upregulation of miR-221/222 in estrogen receptor-α (ERα)-positive cell lines counteracted the effects of E2 depletion or fulvestrant-induced cell death, thus also conferring hormone-independent growth and fulvestrant resistance. In cells with acquired resistance to fulvestrant, miR-221/222 expression was essential for cell growth and cell cycle progression. To identify possible miR-221/222 targets, miR-221- or miR-222- induced alterations in global gene expression profiles and target gene expression at distinct time points were determined, revealing that miR-221/222 overexpression resulted in deregulation of multiple oncogenic signaling pathways previously associated with drug resistance. Activation of β-catenin by miR-221/222 contributed to estrogen-independent growth and fulvestrant resistance, whereas TGF-β-mediated growth inhibition was repressed by the two miRNAs. This first in-depth investigation into the role of miR-221/222 in acquired fulvestrant resistance, a clinically important problem, demonstrates that these two 'oncomirs' may represent promising therapeutic targets for treating hormone-independent, SERD-resistant breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
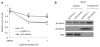
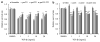
Similar articles
-
A suppressive role of guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-4 inhibited by DNA methylation in the growth of anti-estrogen resistant breast cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2018 Aug 13;18(1):817. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4711-0. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30103729 Free PMC article.
-
Differential microRNA profiles between fulvestrant-resistant and tamoxifen-resistant human breast cancer cells.Anticancer Drugs. 2018 Jul;29(6):539-548. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000623. Anticancer Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29557813
-
Apigenin inhibits antiestrogen-resistant breast cancer cell growth through estrogen receptor-alpha-dependent and estrogen receptor-alpha-independent mechanisms.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jul;7(7):2096-108. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2350. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 18645020 Free PMC article.
-
Roles for miRNAs in endocrine resistance in breast cancer.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015 Oct;22(5):R279-300. doi: 10.1530/ERC-15-0355. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26346768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The silent estrogen receptor--can we make it speak?Cancer Biol Ther. 2009 Mar 15;8(6):485-96. doi: 10.4161/cbt.8.6.7582. Epub 2009 Mar 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19411863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent trends in microRNA research into breast cancer with particular focus on the associations between microRNAs and intrinsic subtypes.J Hum Genet. 2017 Jan;62(1):15-24. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.89. Epub 2016 Jul 21. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 27439682 Review.
-
Mechanisms of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: focus on signaling pathways, miRNAs and genetically based resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Dec 20;14(1):108-45. doi: 10.3390/ijms14010108. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23344024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-221 induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance through PI3K/Akt pathway in human osteosarcoma.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53906. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053906. Epub 2013 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372675 Free PMC article.
-
miR-222 induces Adriamycin resistance in breast cancer through PTEN/Akt/p27kip1 pathway.Tumour Biol. 2016 Nov;37(11):15315-15324. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5341-2. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27699665
-
Phytochemicals modulate carcinogenic signaling pathways in breast and hormone-related cancers.Onco Targets Ther. 2015 Aug 6;8:2053-66. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S83597. eCollection 2015. Onco Targets Ther. 2015. PMID: 26273208 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams BD, Furneaux H, White BA. The micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen receptor-alpha (ERalpha) and represses ERalpha messenger RNA and protein expression in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21:1132–1147. - PubMed
-
- Ali S, Coombes RC. Endocrine-responsive breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:101–112. - PubMed
-
- Ariazi EA, Ariazi JL, Cordera F, Jordan VC. Estrogen receptors as therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6:181–202. - PubMed
-
- Basolo F, Fiore L, Ciardiello F, Calvo S, Fontanini G, Conaldi PG, et al. Response of normal and oncogene-transformed human mammary epithelial cells to transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1): lack of growth-inhibitory effect on cells expressing the simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Int J Cancer. 1994;56:736–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

