Effect of remifentanil on consumption of sevoflurane in entropy monitored general anesthesia
- PMID: 21057612
- PMCID: PMC2966703
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2010.59.4.238
Effect of remifentanil on consumption of sevoflurane in entropy monitored general anesthesia
Abstract
Background: Monitoring of anesthetic depth is important for successful general anesthesia. It is well known that entropy or BIS monitoring assisted titration of anesthetic drugs decreases their consumption. This study evaluated the effect of remifentanil on consumption of sevoflurane during entropy monitored general anesthesia.
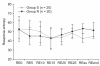
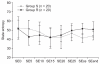
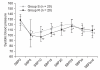
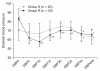
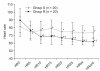
Methods: Patients were randomly assigned to two groups. The R group was administered 0.1 µg/kg/min of remifentanil and inhaled sevoflurane, while the S group was administered only inhaled sevoflurane. Anesthesia was maintained using sevoflurane with nitrous oxide, and entropy was monitored. In both groups, the concentration of sevoflurane was adjusted to keep the state entropy (SE) value between 40 and 60. End-tidal sevoflurane concentration (ET), entropy value, systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and heart rate (HR) were measured at 5 minute intervals, during a 25 minute period after intubation, skin suture and the end of surgery.
Results: ET was significantly lower in the R group than the S group. There were no significant differences in entropy value between R and S groups.
Conclusions: Entropy monitored titration of sevoflurane with remifentanil administration decreased ET with stable hemodynamics.
Keywords: Entropy; Remifentanil; Sevoflurane.
Figures

References
-
- Bruhn J, Bouillon TW, Radulescu L, Hoeft A, Bertaccini E, Shafer SL. Correlation of approximate entropy, bispectral index, and spectral edge frequency 95 (SEF95) with clinical signs of "anesthetic depth" during coadministration of propofol and remifentanil. Anesthesiology. 2003;98:621–627. - PubMed
-
- Vakkuri A, Yli-Hankala A, Talja P, Mustola S, Tolvanen-Laakso H, Sampson T, et al. Time-frequency balanced spectral entropy as a measure of anesthetic drug effect in central nervous system during sevoflurane, propofol, and thiopental anesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2004;48:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt GN, Bischoff P, Standl T, Hellstern A, Teuber O, Schulte Esch J. Comparative evaluation of the Datex-Ohmeda S/5 Entropy Module and the Bispectral Index monitor during propofol-remifentanil anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2004;101:1283–1290. - PubMed
-
- Vanluchene AL, Vereecke H, Thas O, Mortier EP, Shafer SL, Struys MM. Spectral entropy as an electroencephalographic measure of anesthetic drug effect: a comparison with bispectral index and processed midlatency auditory evoked response. Anesthesiology. 2004;101:34–42. - PubMed
-
- Glass PS, Hardman D, Kamiyama Y, Quill TJ, Marton G, Donn KH, et al. Preliminary pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of an ultra-short-acting opioid: remifentanil (GI87084B) Anesth Analg. 1993;77:1031–1040. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

