Study of microscale hydraulic jump phenomenon for hydrodynamic trap-and-release of microparticles
- PMID: 21057671
- PMCID: PMC2973986
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3479052
Study of microscale hydraulic jump phenomenon for hydrodynamic trap-and-release of microparticles
Abstract
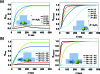
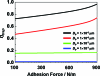
Easy trap-and-release of microparticles is necessary to study biological cellular behavior. The hydraulic jump phenomenon inspired us to conceive a microfluidic device for the hydrodynamic trap-and-release of microparticles. A sudden height increase in a microfluidic channel leads to a dramatic decrease in flow velocity, allowing effective trapping of the microparticles by energy conversion. The trapped particles can be released by stronger inertial force based on simply increasing the flow velocity. We present a systematic, numerical study of trap-and-release of the microparticles using multiphase Navier-Stokes equations. Effect of geometry flow velocity, particle diameter, and adhesion force on trap-and-release was studied.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
