Brief alcohol interventions for mandated college students: comparison of face-to-face counseling and computer-delivered interventions
- PMID: 21059184
- PMCID: PMC3058775
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2010.03193.x
Brief alcohol interventions for mandated college students: comparison of face-to-face counseling and computer-delivered interventions
Abstract
Aims: College students who violate alcohol policies are often mandated to participate in alcohol-related interventions. This study investigated (i) whether such interventions reduced drinking beyond the sanction alone, (ii) whether a brief motivational intervention (BMI) was more efficacious than two computer-delivered interventions (CDIs) and (iii) whether intervention response differed by gender.
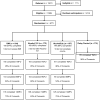
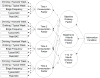
Design: Randomized controlled trial with four conditions [brief motivation interventions (BMI), Alcohol 101 Plus™, Alcohol Edu for Sanctions(®), delayed control] and four assessments (baseline, 1, 6 and 12 months).
Setting: Private residential university in the United States.
Participants: Students (n = 677; 64% male) who had violated campus alcohol policies and were sanctioned to participate in a risk reduction program.
Measurements: Consumption (drinks per heaviest and typical week, heavy drinking frequency, peak and typical blood alcohol concentration), alcohol problems and recidivism.
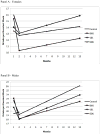
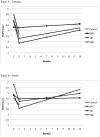
Findings: Piecewise latent growth models characterized short-term (1-month) and longer-term (1-12 months) change. Female but not male students reduced drinking and problems in the control condition. Males reduced drinking and problems after all interventions relative to control, but did not maintain these gains. Females reduced drinking to a greater extent after a BMI than after either CDI, and maintained reductions relative to baseline across the follow-up year. No differences in recidivism were found.
Conclusions: Male and female students responded differently to sanctions for alcohol violations and to risk reduction interventions. BMIs optimized outcomes for both genders. Male students improved after all interventions, but female students improved less after CDIs than after BMI. Intervention effects decayed over time, especially for males.
© 2010 The Authors, Addiction © 2010 Society for the Study of Addiction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Is it time to start discussing what type of computer-delivered intervention?Addiction. 2011 Aug;106(8):1534. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03439.x. Epub 2011 May 27. Addiction. 2011. PMID: 21623983 No abstract available.
-
Is it time to start focusing on the content of computer-delivered interventions?Addiction. 2011 Oct;106(10):1871. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03539.x. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Addiction. 2011. PMID: 21793973 No abstract available.
References
-
- Office of Applied Studies. Underage Alcohol Use among Full-Time College Students. The NSDUH Report [serial on the Internet] 2006;(31)
-
- Doumas DM, McKinley LL, Book P. Evaluation of two Web-based alcohol interventions for mandated college students. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2009;36(1):65–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

