Identification of novel biomarker candidates by proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with moyamoya disease using SELDI-TOF-MS
- PMID: 21059247
- PMCID: PMC2992492
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2377-10-112
Identification of novel biomarker candidates by proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid from patients with moyamoya disease using SELDI-TOF-MS
Abstract
Background: Moyamoya disease (MMD) is an uncommon cerebrovascular condition with unknown etiology characterized by slowly progressive stenosis or occlusion of the bilateral internal carotid arteries associated with an abnormal vascular network. MMD is a major cause of stroke, specifically in the younger population. Diagnosis is based on only radiological features as no other clinical data are available. The purpose of this study was to identify novel biomarker candidate proteins differentially expressed in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of patients with MMD using proteomic analysis.
Methods: For detection of biomarkers, CSF samples were obtained from 20 patients with MMD and 12 control patients. Mass spectral data were generated by surface-enhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF-MS) with an anion exchange chip in three different buffer conditions. After expression difference mapping was undertaken using the obtained protein profiles, a comparative analysis was performed.
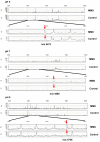
Results: A statistically significant number of proteins (34) were recognized as single biomarker candidate proteins which were differentially detected in the CSF of patients with MMD, compared to the control patients (p < 0.05). All peak intensity profiles of the biomarker candidates underwent classification and regression tree (CART) analysis to produce prediction models. Two important biomarkers could successfully classify the patients with MMD and control patients.
Conclusions: In this study, several novel biomarker candidate proteins differentially expressed in the CSF of patients with MMD were identified by a recently developed proteomic approach. This is a pilot study of CSF proteomics for MMD using SELDI technology. These biomarker candidates have the potential to shed light on the underlying pathogenesis of MMD.
Figures


References
-
- Suzuki J, Takaku A. Cerebrovascular "moyamoya" disease. Disease showing abnormal net-like vessels in base of brain. Arch Neurol. 1969;20:288–299. - PubMed
-
- Mineharu Y, Takenaka K, Yamakawa H, Inoue K, Ikeda H, Kikuta KI, Takagi Y, Nozaki K, Hashimoto N, Koizumi A. Inheritance pattern of familial moyamoya disease: autosomal dominant mode and genomic imprinting. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77:1025–1029. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.096040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

