Regulation of sonic hedgehog-GLI1 downstream target genes PTCH1, Cyclin D2, Plakoglobin, PAX6 and NKX2.2 and their epigenetic status in medulloblastoma and astrocytoma
- PMID: 21059263
- PMCID: PMC2989332
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-614
Regulation of sonic hedgehog-GLI1 downstream target genes PTCH1, Cyclin D2, Plakoglobin, PAX6 and NKX2.2 and their epigenetic status in medulloblastoma and astrocytoma
Abstract
Background: The Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway is critical for cell growth and differentiation. Impairment of this pathway can result in both birth defects and cancer. Despite its importance in cancer development, the Shh pathway has not been thoroughly investigated in tumorigenesis of brain tumors. In this study, we sought to understand the regulatory roles of GLI1, the immediate downstream activator of the Shh signaling pathway on its downstream target genes PTCH1, Cyclin D2, Plakoglobin, NKX2.2 and PAX6 in medulloblastoma and astrocytic tumors.
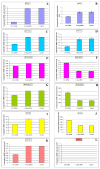
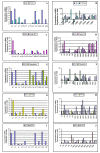
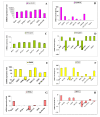
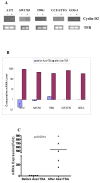
Methods: We silenced GLI1 expression in medulloblastoma and astrocytic cell lines by transfection of siRNA against GLI1. Subsequently, we performed RT-PCR and quantitative real time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) to assay the expression of downstream target genes PTCH1, Cyclin D2, Plakoglobin, NKX2.2 and PAX6. We also attempted to correlate the pattern of expression of GLI1 and its regulated genes in 14 cell lines and 41 primary medulloblastoma and astrocytoma tumor samples. We also assessed the methylation status of the Cyclin D2 and PTCH1 promoters in these 14 cell lines and 58 primary tumor samples.
Results: Silencing expression of GLI1 resulted up-regulation of all target genes in the medulloblastoma cell line, while only PTCH1 was up-regulated in astrocytoma. We also observed methylation of the cyclin D2 promoter in a significant number of astrocytoma cell lines (63%) and primary astrocytoma tumor samples (32%), but not at all in any medulloblastoma samples. PTCH1 promoter methylation was less frequently observed than Cyclin D2 promoter methylation in astrocytomas, and not at all in medulloblastomas.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate different regulatory mechanisms of Shh-GLI1 signaling. These differences vary according to the downstream target gene affected, the origin of the tissue, as well as epigenetic regulation of some of these genes.
Figures




References
-
- Dahmane N, Ruiz i Altaba A. Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development. 1999;126:3089–3100. - PubMed
-
- Mo R, Freer AM, Zinyk DL, Crackower MA, Michaud J, Heng HH, Chik KW, Shi XM, Tsui LC, Cheng SH, Joyner AL, Hui C. Specific and redundant functions of Gli2 and Gli3 zinc finger genes in skeletal patterning and development. Development. 1997;124:113–123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

