Mycophenolate mofetil as maintenance therapy for proliferative lupus nephritis: a long-term observational prospective study
- PMID: 21059275
- PMCID: PMC3046515
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3184
Mycophenolate mofetil as maintenance therapy for proliferative lupus nephritis: a long-term observational prospective study
Abstract
Introduction: While the role of mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) in the management of lupus nephritis has been increasingly recognized, limited information is available regarding its efficacy and safety as a long-term maintenance treatment. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety profile of MMF as maintenance therapy for proliferative lupus nephritis.
Methods: Thirty-three consecutive patients with proliferative lupus nephritis received induction therapy with five to seven monthly intravenous (iv) pulses of cyclophosphamide (CYC) plus iv steroids followed by oral MMF 2 g/day as maintenance therapy for a median time of 29 months (range 9 to 71 months). Primary end points were the achievement of renal remission, complete renal remission, disease remission - renal and extrarenal -, the occurrence of renal relapse, chronic renal failure and death. Secondary end points were the extrarenal disease activity and drug adverse events. The clinical and laboratory parameters were compared during follow-up by means of nonparametric statistical tests. Time to event analysis was performed according to the Kaplan-Meier method.
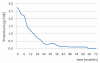
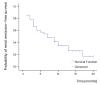
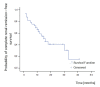
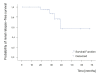
Results: A significant improvement of all renal parameters was observed at the end of the induction treatment and at the latest follow-up compared to baseline. The rate of patients achieving renal remission until the end of follow-up was 73%, whereas that of complete renal remission was 58%. The median survival times in the Kaplan-Meier analyses were 7 and 16 months, respectively. Remission was maintained in all but four (12%) patients who relapsed within 19 to 39 months after initial response. At the end of follow-up, 51% of the patients had reached disease remission. The median survival time of disease remission was 18 months. Extrarenal manifestations were well controlled in most of the patients. In one patient receiving MMF, extrarenal activity led to treatment discontinuation. Non life-threatening drug adverse events developed in 18 patients (58%) and included infections, amenorrhea, myelotoxicity, gastrointestinal complications, hypercholesterolemia, alopecia and drug intolerance. None of the patients developed chronic renal insufficiency or died from any cause.
Conclusions: MMF appeared to be efficacious and safe as maintenance treatment for proliferative lupus nephritis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Maintenance therapies for proliferative lupus nephritis: mycophenolate mofetil, azathioprine and intravenous cyclophosphamide.Lupus. 2005;14 Suppl 1:s33-8. doi: 10.1191/0961203305lu2115oa. Lupus. 2005. PMID: 15803929 Clinical Trial.
-
Sequential therapies for proliferative lupus nephritis.N Engl J Med. 2004 Mar 4;350(10):971-80. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa031855. N Engl J Med. 2004. PMID: 14999109 Clinical Trial.
-
The use of low-dose cyclophosphamide followed by AZA/MMF treatment in childhood lupus nephritis.Pediatr Nephrol. 2010 Jan;25(1):111-7. doi: 10.1007/s00467-009-1291-x. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Pediatr Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 19727839
-
Induction and maintenance treatment of proliferative lupus nephritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Am J Kidney Dis. 2013 Jan;61(1):74-87. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.08.041. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013. PMID: 23182601
-
What is the value of mycophenolate mofetil as induction and maintenance therapy in lupus nephritis?Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009 May;21(3):256-61. doi: 10.1097/bor.0b013e32832a0698. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19399995 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of mycophenolate mofetil therapy in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 7;10(1):16727. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-73882-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33028926 Free PMC article.
-
A phase I study of autologous mesenchymal stromal cells for severe steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome.JCI Insight. 2023 Sep 22;8(18):e169424. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.169424. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37561590 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
B-cell depletion in the treatment of lupus nephritis.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012 Sep;8(9):505-14. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.141. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22801948 Review.
-
Optimizing the dose of mycophenolate mofetil for the maintenance treatment of lupus nephritis by therapeutic drug monitoring.Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Jan;34(1):171-4. doi: 10.1007/s10067-014-2786-9. Epub 2014 Sep 25. Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25249327
-
Immunosuppression With Mycophenolate Mofetil Attenuates Hypertension in an Experimental Model of Autoimmune Disease.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Feb 27;6(3):e005394. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005394. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28242635 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Illei GG, Austin HA, Crane M, Collins L, Gourley MF, Yarboro CH, Vaughan EM, Kuroiwa T, Danning CL, Steinberg AD, Klippel JH, Balow JE, Boumpas DT. Combination therapy with pulse cyclophosphamide plus pulse methylprednisolone improves long-term renal outcome without adding toxicity in patients with lupus nephritis. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:248–257. - PubMed
-
- Ioannidis JPA, Katsifis GE, Tzioufas AG, Moutsopoulos H. Predictors of sustained amenorrhea from pulsed intravenous cyclophosphamide in premenopausal women with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:2129–2135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

