Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac remodeling
- PMID: 21059352
- PMCID: PMC3072437
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2010.10.033
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac remodeling
Abstract
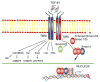
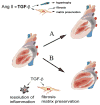
Myocardial TGF-β expression is upregulated in experimental models of myocardial infarction and cardiac hypertrophy, and in patients with dilated or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Through its effects on cardiomyocytes, mesenchymal and immune cells, TGF-β plays an important role in the pathogenesis of cardiac remodeling and fibrosis. TGF-β overexpression in the mouse heart is associated with fibrosis and hypertrophy. Endogenous TGF-β plays an important role in the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrotic and hypertrophic remodeling, and modulates matrix metabolism in the pressure-overloaded heart. In the infarcted heart, TGF-β deactivates inflammatory macrophages, while promoting myofibroblast transdifferentiation and matrix synthesis through Smad3-dependent pathways. Thus, TGF-β may serve as the "master switchThis article is part of a special issue entitled "Key Signaling Molecules in Hypertrophy and Heart Failure". for the transition of the infarct from the inflammatory phase to formation of the scar. Because of its crucial role in cardiac remodeling, the TGF-β system may be a promising therapeutic target for patients with heart failure. However, efforts to translate these concepts into therapeutic strategies, in order to prevent cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis, are hampered by the complex, pleiotropic and diverse effects of TGF-β signaling, by concerns regarding deleterious actions of TGF-β inhibition and by the possibility of limited benefit in patients receiving optimal treatment with ACE inhibitors and β-adrenergic blockers. Dissection of the pathways responsible for specific TGF-β-mediated actions and understanding of cell-specific actions of TGF-β are needed to design optimal therapeutic strategies. This article is part of a special issue entitled "Key Signaling Molecules in Hypertrophy and Heart Failure".
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Schiller M, Javelaud D, Mauviel A. TGF-beta-induced SMAD signaling and gene regulation: consequences for extracellular matrix remodeling and wound healing. J Dermatol Sci. 2004;35:83–92. - PubMed
-
- Annes JP, Munger JS, Rifkin DB. Making sense of latent TGFbeta activation. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:217–24. - PubMed
-
- Koli K, Saharinen J, Hyytiainen M, Penttinen C, Keski-Oja J. Latency, activation, and binding proteins of TGF-beta. Microsc Res Tech. 2001;52:354–62. - PubMed
-
- Murphy-Ullrich JE, Poczatek M. Activation of latent TGF-beta by thrombospondin-1: mechanisms and physiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000;11:59–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

