Physiological and pathological population dynamics of circulating human red blood cells
- PMID: 21059904
- PMCID: PMC2996693
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1012747107
Physiological and pathological population dynamics of circulating human red blood cells
Abstract
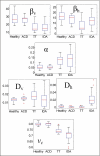
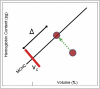
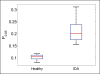
The systems controlling the number, size, and hemoglobin concentrations of populations of human red blood cells (RBCs), and their dysregulation in anemia, are poorly understood. After release from the bone marrow, RBCs undergo reduction in both volume and total hemoglobin content by an unknown mechanism [Lew VL, et al. (1995) Blood 86:334-341; Waugh RE, et al. (1992) Blood 79:1351-1358]; after ∼120 d, responding to an unknown trigger, they are removed. We used theory from statistical physics and data from the hospital clinical laboratory [d'Onofrio G, et al. (1995) Blood 85:818-823] to develop a master equation model for RBC maturation and clearance. The model accurately identifies patients with anemia and distinguishes thalassemia-trait anemia from iron-deficiency anemia. Strikingly, it also identifies many pre-anemic patients several weeks before anemia becomes clinically detectable. More generally we illustrate how clinical laboratory data can be used to develop and to test a dynamic model of human pathophysiology with potential clinical utility.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.M.H. and L.M. are listed as inventors on a patent application related to this manuscript submitted by their institutions.
Figures
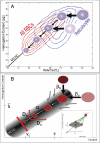
 .
.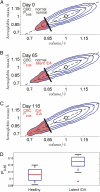

 ) along this line.
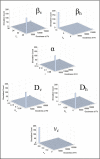
) along this line.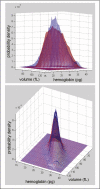
References
-
- Fauci AS. In: Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine. 17th Ed. Fauci AS, et al., editors. New York: McGraw–Hill Medical; 2008.
-
- d'Onofrio G, et al. Simultaneous measurement of reticulocyte and red blood cell indices in healthy subjects and patients with microcytic and macrocytic anemia. Blood. 1995;85:818–823. - PubMed
-
- Gifford SC, Derganc J, Shevkoplyas SS, Yoshida T, Bitensky MW. A detailed study of time-dependent changes in human red blood cells: From reticulocyte maturation to erythrocyte senescence. Br J Haematol. 2006;135:395–404. - PubMed
-
- Waugh RE, et al. Rheologic properties of senescent erythrocytes: Loss of surface area and volume with red blood cell age. Blood. 1992;79:1351–1358. - PubMed
-
- Willekens FL, et al. Hemoglobin loss from erythrocytes in vivo results from spleen-facilitated vesiculation. Blood. 2003;101:747–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

