Bisphenol A impairs the double-strand break repair machinery in the germline and causes chromosome abnormalities
- PMID: 21059909
- PMCID: PMC2996676
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1010386107
Bisphenol A impairs the double-strand break repair machinery in the germline and causes chromosome abnormalities
Abstract
Bisphenol A (BPA) is a highly prevalent constituent of plastics that has been associated with diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and an increased risk of miscarriages in humans. In mice, BPA exposure disrupts the process of meiosis; however, analysis of the affected molecular pathways is lagging and has been particularly challenging. Here we show that exposure of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans to BPA, at internal concentrations consistent with mammalian models, causes increased sterility and embryonic lethality. BPA exposure results in impaired chromosome synapsis and disruption of meiotic double-strand break repair (DSBR) progression. BPA carries an anti-estrogenic activity in the germline and results in germline-specific down-regulation of DSBR genes, thereby impairing maintenance of genomic integrity during meiosis. C. elegans therefore constitutes a model of remarkable relevance to mammals with which to assess how our chemical landscape affects germ cells and meiosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

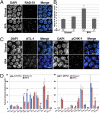

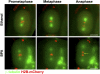
References
-
- Hunt PA, Hassold TJ. Human female meiosis: What makes a good egg go bad? Trends Genet. 2008;24:86–93. - PubMed
-
- Christianson RE, Sherman SL, Torfs CP. Maternal meiosis II nondisjunction in trisomy 21 is associated with maternal low socioeconomic status. Genet Med. 2004;6:487–494. - PubMed
-
- Hunt PA. Meiosis in mammals: Recombination, non-disjunction and the environment. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:574–577. - PubMed
-
- National Toxicology Program NTP-CERHR monograph on the potential human reproductive and developmental effects of Bisphenol A. NTP CERHR MON. 2008;(22):i–III1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

