Advances in translational research in neuro-oncology
- PMID: 21059986
- PMCID: PMC3109723
- DOI: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.293
Advances in translational research in neuro-oncology
Abstract
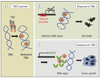
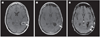
During the last decade, we have witnessed several key advances in the field of neuro-oncology. First, there were conceptual advances in the molecular and cell biology of malignant gliomas including the discovery in 2004 of brain tumor stem cells. Second, the Cancer Genome Atlas project has been extremely useful in the discovery of new molecular markers, including mutations in the IDH1 gene, and has led to a new classification of gliomas based on the differentiation status and mesenchymal transformation. In addition, use of the 1p/19q marker and O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase methylation status have been identified as guides for patient selection for therapies and represent the first steps toward personalized medicine for treating gliomas. Finally, progress has been made in treatment strategies including the establishment of temozolomide as the criterion standard for treating gliomas, the adoption of bevacizumab in the clinical setting, and developments in experimental biological therapies including cancer vaccines and oncolytic adenoviruses.
Figures

References
-
- Galli R, Binda E, Orfanelli U, et al. Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64(19):7011–7021. - PubMed
-
- Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, et al. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature. 2004;432(7015):396–401. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444(7120):756–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

