A lifespan analysis of intraneocortical connections and gene expression in the mouse II
- PMID: 21060113
- PMCID: PMC3140181
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhq213
A lifespan analysis of intraneocortical connections and gene expression in the mouse II
Abstract
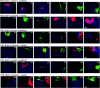
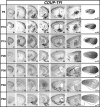
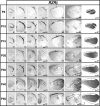
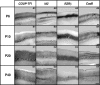
The mammalian neocortex contains an intricate processing network of multiple sensory and motor areas that allows the animal to engage in complex behaviors. These anatomically and functionally unique areas and their distinct connections arise during early development, through a process termed arealization. Both intrinsic, activity-independent and extrinsic, activity-dependent mechanisms drive arealization, much of which occurs during the areal patterning period (APP) from late embryogenesis to early postnatal life. How areal boundaries and their connections develop and change from infancy to adulthood is not known. Additionally, the adult patterns of sensory and motor ipsilateral intraneocortical connections (INCs) have not been thoroughly characterized in the mouse. In this report and its companion (I), we present the first lifespan analysis of ipsilateral INCs among multiple sensory and motor regions in mouse. We describe the neocortical expression patterns of several developmentally regulated genes that are of central importance to studies investigating the molecular regulation of arealization, from postnatal day (P) 6 to P50. In this study, we correlate the boundaries of gene expression patterns with developing areal boundaries across a lifespan, in order to better understand the nature of gene-areal relationships from early postnatal life to adulthood.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Rapid Changes in Cortical and Subcortical Brain Regions after Early Bilateral Enucleation in the Mouse.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 9;10(10):e0140391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140391. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26452243 Free PMC article.
-
A lifespan analysis of intraneocortical connections and gene expression in the mouse I.Cereb Cortex. 2011 Jun;21(6):1311-30. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq212. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Cereb Cortex. 2011. PMID: 21060110 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral enucleation alters gene expression and intraneocortical connections in the mouse.Neural Dev. 2012 Jan 30;7:5. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-7-5. Neural Dev. 2012. PMID: 22289655 Free PMC article.
-
Gene networks controlling early cerebral cortex arealization.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Feb;23(4):847-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04634.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16519650 Review.
-
Neocortical areas, layers, connections, and gene expression.Neurosci Res. 2006 May;55(1):11-27. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2006.02.006. Epub 2006 Mar 20. Neurosci Res. 2006. PMID: 16546282 Review.
Cited by
-
Rapid Changes in Cortical and Subcortical Brain Regions after Early Bilateral Enucleation in the Mouse.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 9;10(10):e0140391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140391. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26452243 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic Acid-Related Orphan Receptors (RORs): Regulatory Functions in Immunity, Development, Circadian Rhythm, and Metabolism.Nucl Receptor Res. 2015;2:101185. doi: 10.11131/2015/101185. Epub 2015 Dec 16. Nucl Receptor Res. 2015. PMID: 26878025 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the development of cortex-wide gene expression patterns between two species in a common reference frame.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Oct 11;119(41):e2113896119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2113896119. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 36201538 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal Ethanol Exposure and Neocortical Development: A Transgenerational Model of FASD.Cereb Cortex. 2018 Aug 1;28(8):2908-2921. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx168. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 29106518 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal ethanol exposure disrupts intraneocortical circuitry, cortical gene expression, and behavior in a mouse model of FASD.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 27;33(48):18893-905. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3721-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24285895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armentano M, Chou SJ, Tomassy GS, Leingärtner A, O'Leary DD, Studer M. COUP-TFI regulates the balance of cortical patterning between frontal/motor and sensory areas. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:1277–1286. - PubMed
-
- Bayer SA, Altman J. Neocortical development. New York: Raven; 1991.
-
- Berardi N, Pizzorusso T, Maffei L. Critical periods during sensory development. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2000;10:138–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

