Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in the genomic era
- PMID: 21060334
- PMCID: PMC3135416
- DOI: 10.1038/nrrheum.2010.176
Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in the genomic era
Abstract
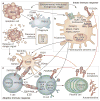
Our understanding of the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has been rapidly advanced using large-scale, case-control, candidate gene studies as well as genome-wide association studies during the past 3 years. These techniques have identified more than 30 robust genetic associations with SLE including genetic variants of HLA and Fcγ receptor genes, IRF5, STAT4, PTPN22, TNFAIP3, BLK, BANK1, TNFSF4 and ITGAM. Most SLE-associated gene products participate in key pathogenic pathways, including Toll-like receptor and type I interferon signaling pathways, immune regulation pathways and those that control the clearance of immune complexes. Disease-associated loci that have not yet been demonstrated to have important functions in the immune system might provide new clues to the underlying molecular mechanisms that contribute to the pathogenesis or progression of SLE. Of note, genetic risk factors that are shared between SLE and other immune-related diseases highlight common pathways in the pathophysiology of these diseases, and might provide innovative molecular targets for therapeutic interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Deapen D, et al. A revised estimate of twin concordance in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992;35:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Alarcón-Segovia D, et al. Familial aggregation of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases in 1,177 lupus patients from the GLADEL cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:1138–1147. - PubMed
-
- Nath SK, et al. A nonsynonymous functional variant in integrin-alpha(M) (encoded by ITGAM) is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 2008;40:152–154. - PubMed
-
- Hom G, et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:900–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

