The meiotic recombination checkpoint suppresses NHK-1 kinase to prevent reorganisation of the oocyte nucleus in Drosophila
- PMID: 21060809
- PMCID: PMC2965759
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001179
The meiotic recombination checkpoint suppresses NHK-1 kinase to prevent reorganisation of the oocyte nucleus in Drosophila
Abstract
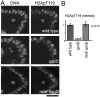
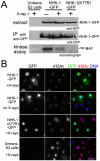
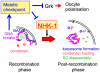
The meiotic recombination checkpoint is a signalling pathway that blocks meiotic progression when the repair of DNA breaks formed during recombination is delayed. In comparison to the signalling pathway itself, however, the molecular targets of the checkpoint that control meiotic progression are not well understood in metazoans. In Drosophila, activation of the meiotic checkpoint is known to prevent formation of the karyosome, a meiosis-specific organisation of chromosomes, but the molecular pathway by which this occurs remains to be identified. Here we show that the conserved kinase NHK-1 (Drosophila Vrk-1) is a crucial meiotic regulator controlled by the meiotic checkpoint. An nhk-1 mutation, whilst resulting in karyosome defects, does so independent of meiotic checkpoint activation. Rather, we find unrepaired DNA breaks formed during recombination suppress NHK-1 activity (inferred from the phosphorylation level of one of its substrates) through the meiotic checkpoint. Additionally DNA breaks induced by X-rays in cultured cells also suppress NHK-1 kinase activity. Unrepaired DNA breaks in oocytes also delay other NHK-1 dependent nuclear events, such as synaptonemal complex disassembly and condensin loading onto chromosomes. Therefore we propose that NHK-1 is a crucial regulator of meiosis and that the meiotic checkpoint suppresses NHK-1 activity to prevent oocyte nuclear reorganisation until DNA breaks are repaired.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Keeney S, Giroux CN, Kleckner N. Meiosis-specific DNA double-strand breaks are catalyzed by Spo11, a member of a widely conserved protein family. Cell. 1997;88:375–384. - PubMed
-
- Dernburg AF, McDonald K, Moulder G, Barstead R, Dresser M, et al. Meiotic recombination in C. elegans initiates by a conserved mechanism and is dispensable for homologous chromosome synapsis. Cell. 1998;94:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Keeney S, Baudat F, Angeles M, Zhou ZH, Copeland NG, et al. A mouse homolog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae meiotic recombination DNA transesterase Spo11p. Genomics. 1999;61:170–182. - PubMed
-
- Page SL, Hawley RS. The genetics and molecular biology of the synaptonemal complex. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:525–558. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

