DSIF and RNA polymerase II CTD phosphorylation coordinate the recruitment of Rpd3S to actively transcribed genes
- PMID: 21060864
- PMCID: PMC2965751
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001173
DSIF and RNA polymerase II CTD phosphorylation coordinate the recruitment of Rpd3S to actively transcribed genes
Abstract
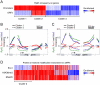
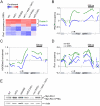
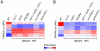
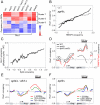
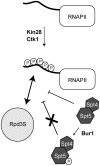
Histone deacetylase Rpd3 is part of two distinct complexes: the large (Rpd3L) and small (Rpd3S) complexes. While Rpd3L targets specific promoters for gene repression, Rpd3S is recruited to ORFs to deacetylate histones in the wake of RNA polymerase II, to prevent cryptic initiation within genes. Methylation of histone H3 at lysine 36 by the Set2 methyltransferase is thought to mediate the recruitment of Rpd3S. Here, we confirm by ChIP-Chip that Rpd3S binds active ORFs. Surprisingly, however, Rpd3S is not recruited to all active genes, and its recruitment is Set2-independent. However, Rpd3S complexes recruited in the absence of H3K36 methylation appear to be inactive. Finally, we present evidence implicating the yeast DSIF complex (Spt4/5) and RNA polymerase II phosphorylation by Kin28 and Ctk1 in the recruitment of Rpd3S to active genes. Taken together, our data support a model where Set2-dependent histone H3 methylation is required for the activation of Rpd3S following its recruitment to the RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Shahbazian MD, Grunstein M. Functions of site-specific histone acetylation and deacetylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:75–100. - PubMed
-
- Huang D, Kaluarachchi S, Van Dyk D, Friesen H, Sopko R, et al. Dual regulation by pairs of cyclin-dependent protein kinases and histone deacetylases controls G1 transcription in budding yeast. PLoS Biol. 2009;7:e1000188. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000188. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

