Bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation for the treatment of insulin-dependent diabetes
- PMID: 21060973
- PMCID: PMC2989787
- DOI: 10.1900/RDS.2010.7.144
Bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation for the treatment of insulin-dependent diabetes
Abstract
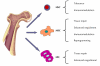
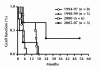
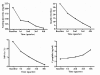
The bone marrow is an invaluable source of adult pluripotent stem cells, as it gives rise to hematopoietic stem cells, endothelial progenitor cells, and mesenchymal cells, amongst others. The use of bone marrow-derived stem cell (BMC) transplantation (BMT) may be of assistance in achieving tissue repair and regeneration, as well as in modulating immune responses in the context of autoimmunity and transplantation. Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the effects of BMC to preserve functional beta-cell mass in subjects with type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and to favor engraftment and survival of transplanted islets. Additional trials are evaluating the impact of BMT (i.e., mesenchymal stem cells) on the progression of diabetes complications. This article reviews the progress in the field of BMC for the treatment of subjects with insulin-dependent diabetes, and summarizes clinical data of pilot studies performed over the last two decades at our research center by combining allogeneic islet transplantation with donor-specific BMC. Clinical data is summarized from pilot studies performed at our research center over the last two decades.
Figures
References
-
- Ricordi C. Islet transplantation: a brave new world. Diabetes. 2003;52:1595–1603. - PubMed
-
- Mineo D, Ricordi C, Xu X, Pileggi A, Garcia-Morales R, Khan A, Baidal DA, Han D, Monroy K, Miller J. et al. Combined islet and hematopoietic stem cell allotransplantation: a clinical pilot trial to induce chimerism and graft tolerance. Am J Transplant. 2008;8:1262–1274. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou PY, Milliat-Guittard L, Wojtusciszyn A, Kessler L, Toso C, Baertschiger R, Debaty I, Badet L, Penfornis A, Thivolet C. et al. Quality of life after islet transplantation: data from the GRAGIL 1 and 2 trials. Diabet Med. 2009;26:617–621. - PubMed
-
- Cure P, Pileggi A, Froud T, Messinger S, Faradji RN, Baidal DA, Cardani R, Curry A, Poggioli R, Pugliese A. et al. Improved metabolic control and quality of life in seven patients with type 1 diabetes following islet after kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2008;85:801–812. - PubMed
-
- Poggioli R, Faradji RN, Ponte G, Betancourt A, Messinger S, Baidal DA, Froud T, Ricordi C, Alejandro R. Quality of life after islet transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2006;6:371–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1R01 EB008009-02/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK056953/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK025802/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK059993-04/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U42 RR016603/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01RR16587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R43DK083832/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK070460/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21DK076098-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01 DK70460-02/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056953/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK025802/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HD060195/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 1DP2DK083096-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 DK083096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008009/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK25802-24/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R43 DK083832/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK55347/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5U42RR016603-08S1/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21HD060195-01/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK076098/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01DK56953-05/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
