Sleep restriction during pregnancy: hypertension and renal abnormalities in young offspring rats
- PMID: 21061858
- PMCID: PMC2941422
- DOI: 10.1093/sleep/33.10.1357
Sleep restriction during pregnancy: hypertension and renal abnormalities in young offspring rats
Abstract
Study objectives: Because the maternal environment can affect several physiological functions of the newborn, the aim of the present study was to examine the impact of sleep restriction during pregnancy on renal morphology and function in young offspring.
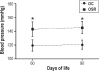
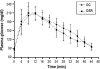
Design: Female 3-month-old Wistar rats were divided in 2 experimental groups: C (control) and SR (sleep restriction between the 14th and 20th day of pregnancy). Pregnancy was confirmed by vaginal smear. SR females were subjected to sleep restriction by the multiple platform technique for 20 h daily. After birth, only male litters (6 for each mother) were selected and designated OC (offspring from C) and OSR (offspring from SR). At 2 months of age, blood pressure (BP) was measured by tail plethysmography; at 3 months the renal plasma flow (RPF), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), glomerular area, and number of glomeruli per mm3 were evaluated.
Measurements and results: Offspring from SR had higher systolic blood pressure than OC. In this group (OSR), we also observed significant increase in RPF and GFR, enlarged glomeruli diameter, and reduced number of glomeruli per mm3 of renal tissue.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that sleep restriction during pregnancy is able to modify renal development, resulting in morphologic and functional alterations in young offspring.
Figures
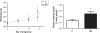

Similar articles
-
Sleep restriction during pregnancy and its effects on blood pressure and renal function among female offspring.Physiol Rep. 2016 Aug;4(16):e12888. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12888. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796270 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic sleep restriction during pregnancy--repercussion on cardiovascular and renal functioning of male offspring.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 18;9(11):e113075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113075. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25405471 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic and Renal Alterations in the Offspring of Sleep-Restricted Mothers During Late Pregnancy.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016 Sep;71(9):521-7. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2016(09)07. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2016. PMID: 27652834 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between maternal global nutrient restriction during pregnancy and offspring kidney structure and function: a systematic review of animal studies.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):F1227-F1235. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00082.2019. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30969805
-
Maternal nutrition and predisposition to later kidney disease.Curr Drug Targets. 2007 Aug;8(8):906-13. doi: 10.2174/138945007781386875. Curr Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 17691927 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for sleep disorders in pregnancy complications: challenges and opportunities.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jan;210(1):3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2013.11.020. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24359866 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Sleep restriction during pregnancy and its effects on blood pressure and renal function among female offspring.Physiol Rep. 2016 Aug;4(16):e12888. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12888. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27796270 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of maternal diabetes on female offspring.Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2014 Oct-Dec;12(4):413-9. doi: 10.1590/S1679-45082014AO3200. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2014. PMID: 25628190 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic sleep restriction during pregnancy--repercussion on cardiovascular and renal functioning of male offspring.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 18;9(11):e113075. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113075. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25405471 Free PMC article.
-
The First Thousand Days: Kidney Health and Beyond.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Oct 6;9(10):1332. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9101332. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34683012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barker DJP. In utero programming of chronic disease. Clin Sci. 1998;95:115–28. - PubMed
-
- Barker DJP, Bagby SP, Hanson MA. Mechanisms of disease: in utero programming in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Nature Clin Prac Nephrology. 2002;2:700–7. - PubMed
-
- Aerts L, Van Assche A. Intra-uterine transmission of disease. Placenta. 2003;24:905–11. - PubMed
-
- Lucas SRR, Costa-Silva VL, Zaladek-Gil F. Effects of intrauterine undernutrition on the renal function of the progeny. Brazilian J Med Biol Res. 1989;22:1303–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

