Early transcriptional events during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells induced by Lim mineralization protein 3
- PMID: 21061915
- PMCID: PMC6043822
- DOI: 10.3727/105221610x12819686555097
Early transcriptional events during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells induced by Lim mineralization protein 3
Abstract
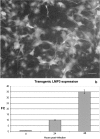
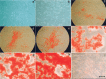
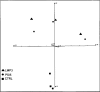
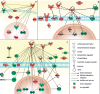
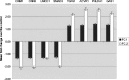
Lim mineralization protein-3 (LMP3) induces osteoblast differentiation by regulating the expression and activity of certain molecules involved in the osteogenic cascade, including those belonging to the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) family. The complete network of molecular events involved in LMP3-mediated osteogenesis is still unknown. The aim of this study was to analyze the genome-wide gene expression profiles in human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSC) induced by exogenous LMP3 to mediate osteogenesis. For this purpose hMSC were transduced with a defective adenoviral vector expressing the human LMP3 gene and microarray analysis was performed 1 day post-adenoviral transduction. Cells transduced with the vector backbone and untransduced cells were used as independent controls in the experiments. Microarray data were independently validated by means of real-time PCR on selected transcripts. The statistical analysis of microarray data produced a list of 263 significantly (p < 0.01) differentially expressed transcripts. The biological interpretation of the results indicated, among the most noteworthy effects, the modulation of genes involved in the TGF-beta1 pathway: 88 genes coding for key regulators of the cell cycle regulatory machinery and 28 genes implicated in the regulation of cell proliferation along with the development of connective, muscular, and skeletal tissues. These results suggested that LMP3 could affect the fine balance between cell proliferation/differentiation of mesenchymal cells mostly by modulating the TGF-beta1 signaling pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Ashburner M.; Ball C. A.; Blake J. A.; Botstein D.; Butler H.; Cherry J. M.; Davis A. P.; Dolinski K.; Dwight S. S.; Eppig J. T.; Harris M. A.; Hill D. P.; Issel-Tarver L.; Kasarskis A.; Lewis S.; Matese J. C.; Richardson J. E.; Ringwald M.; Rubin G. M.; Sherlock G. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 25:25–29; 2000. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boden S. D.; Liu Y.; Hair G. A.; Helms J. A.; Hu D.; Racine M.; Nanes M. S.; Titus L. LMP-1, a LIM-domain protein, mediates BMP-6 effects on bone formation. Endocrinology 139:5125–5134; 1998. - PubMed
-
- Boden S. D.; Titus L.; Hair G.; Liu Y.; Viggeswarapu M.; Nanes M. S.; Baranowski C. Lumbar spine fusion by local gene therapy with a cDNA encoding a novel osteoinductive protein (LMP-1). Spine 23:2486–2492; 1998. - PubMed
-
- Brazma A.; Hingamp P.; Quackenbush J.; Sherlock G.; Spellman P.; Stoeckert C.; Aach J.; Ansorge W.; Ball C. A.; Causton H. C.; Gaasterland T.; Glenisson P.; Holstege F. C.; Kim I. F.; Markowitz V.; Matese J. C.; Parkinson H.; Robinson A.; Sarkans U.; Schulze-Kremer S.; Stewart J.; Taylor R.; Vilo J.; Vingron M. Minimum information about a microarray experiment (MIAME)-toward standards for microarray data. Nat. Genet. 29:365–371; 2001. - PubMed
-
- Bünger M. H.; Langdahl B. L.; Andersen T.; Husted L.; Lind M.; Eriksen E. F.; B?nger C. E. Semiquantitative mRNA measurements of osteoinductive growth factors in human iliac-crest bone: Expression of LMP splice variants in human bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 73:446–454; 2003. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
