Activated-ion electron transfer dissociation improves the ability of electron transfer dissociation to identify peptides in a complex mixture
- PMID: 21062032
- PMCID: PMC3005528
- DOI: 10.1021/ac1020358
Activated-ion electron transfer dissociation improves the ability of electron transfer dissociation to identify peptides in a complex mixture
Abstract
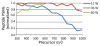
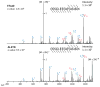
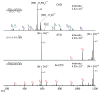
Using a modified electron transfer dissociation (ETD)-enabled quadrupole linear ion trap (QLT) mass spectrometer, we demonstrate the utility of IR activation concomitant with ETD ion-ion reactions (activated-ion ETD, AI-ETD). Analyzing 12 strong cation exchanged (SCX) fractions of a LysC digest of human cell protein extract using ETD, collision-activated dissociation (CAD), and AI-ETD, we find that AI-ETD generates 13 405 peptide spectral matches (PSMs) at a 1% false-discovery rate (1% FDR), surpassing both ETD (7 968) and CAD (10 904). We also analyze 12 SCX fractions of a tryptic digest of human cell protein extract and find that ETD produces 6 234 PSMs, AI-ETD 9 130 PSMs, and CAD 15 209 PSMs. Compared to ETD with supplemental collisional activation (ETcaD), AI-ETD generates ∼80% more PSMs for the whole cell lysate digested with trypsin and ∼50% more PSMs for the whole cell lysate digested with LysC.
Figures

References
-
- Aebersold R, Mann M. Nature. 2003;422:198–207. - PubMed
-
- Coon JJ, Syka JEP, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF. Biotechniques. 2005;38:519. - PubMed
-
- de Godoy LMF, Olsen JV, Cox J, Nielsen ML, Hubner NC, Frohlich F, Walther TC, Mann M. Nature. 2008;455:1251–U1260. - PubMed
-
- Washburn MP, Wolters D, Yates JR. Nature Biotechnology. 2001;19:242–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

