Biocompatible copper(I) catalysts for in vivo imaging of glycans
- PMID: 21062072
- PMCID: PMC3021957
- DOI: 10.1021/ja106553e
Biocompatible copper(I) catalysts for in vivo imaging of glycans
Abstract
The Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) is the standard method for bioorthogonal conjugation. However, current Cu(I) catalyst formulations are toxic, hindering their use in living systems. Here we report that BTTES, a tris(triazolylmethyl)amine-based ligand for Cu(I), promotes the cycloaddition reaction rapidly in living systems without apparent toxicity. This catalyst allows, for the first time, noninvasive imaging of fucosylated glycans during zebrafish early embryogenesis. We microinjected embryos with alkyne-bearing GDP-fucose at the one-cell stage and detected the metabolically incorporated unnatural sugars using the biocompatible click chemistry. Labeled glycans could be imaged in the enveloping layer of zebrafish embryos between blastula and early larval stages. This new method paves the way for rapid, noninvasive imaging of biomolecules in living organisms.
Figures




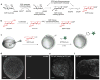
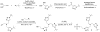
References
-
- Kolb HC, Finn MG, Sharpless KB. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2001;40:2004–2021. - PubMed
-
- Baskin JM, Bertozzi CR. Qsar Comb Sci. 2007;26:1211–1219.
-
- Wang L, Schultz PG. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2004;44:34–66. - PubMed
-
- Laughlin ST, Agard NJ, Baskin JM, Carrico IS, Chang PV, Ganguli AS, Hangauer MJ, Lo A, Prescher JA, Bertozzi CR. Methods Enzymol. 2006;415:230–250. - PubMed
-
- Dieterich DC, Lee JJ, Link AJ, Graumann J, Tirrell DA, Schuman EM. Nat Protc. 2007;2:532–540. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

