Analysis of in situ pre-mRNA targets of human splicing factor SF1 reveals a function in alternative splicing
- PMID: 21062807
- PMCID: PMC3061054
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq1042
Analysis of in situ pre-mRNA targets of human splicing factor SF1 reveals a function in alternative splicing
Abstract
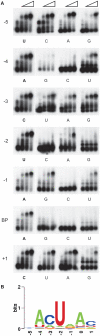
The conserved pre-mRNA splicing factor SF1 is implicated in 3' splice site recognition by binding directly to the intron branch site. However, because SF1 is not essential for constitutive splicing, its role in pre-mRNA processing has remained mysterious. Here, we used crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) to analyze short RNAs directly bound by human SF1 in vivo. SF1 bound mainly pre-mRNAs, with 77% of target sites in introns. Binding to target RNAs in vitro was dependent on the newly defined SF1 binding motif ACUNAC, strongly resembling human branch sites. Surprisingly, the majority of SF1 binding sites did not map to the expected position near 3' splice sites. Instead, target sites were distributed throughout introns, and a smaller but significant fraction occurred in exons within coding and untranslated regions. These data suggest a more complex role for SF1 in splicing regulation. Indeed, SF1 silencing affected alternative splicing of endogenous transcripts, establishing a previously unexpected role for SF1 and branch site-like sequences in splice site selection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Splicing factors SF1 and U2AF associate in extraspliceosomal complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 May;28(9):3045-57. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02015-07. Epub 2008 Feb 19. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18285458 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of phosphorylated SF1 bound to U2AF⁶⁵ in an essential splicing factor complex.Structure. 2013 Feb 5;21(2):197-208. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2012.10.020. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Structure. 2013. PMID: 23273425 Free PMC article.
-
RNA induces conformational changes in the SF1/U2AF65 splicing factor complex.J Mol Biol. 2011 Feb 4;405(5):1128-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.11.054. Epub 2010 Dec 10. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21146534 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-protein interactions that regulate pre-mRNA splicing.Gene Expr. 2002;10(1-2):79-92. Gene Expr. 2002. PMID: 11868989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing: factors involved in splice site selection.J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107 ( Pt 1):1-7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.1. J Cell Sci. 1994. PMID: 8175901 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Modulation of D3R Splicing, Signaling, and Expression by D1R through PKA→PTB Phosphorylation.Biomedicines. 2024 Jan 17;12(1):206. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12010206. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38255311 Free PMC article.
-
SF1 Phosphorylation Enhances Specific Binding to U2AF65 and Reduces Binding to 3'-Splice-Site RNA.Biophys J. 2016 Dec 20;111(12):2570-2586. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.11.007. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 28002734 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of a U2 snRNA gene causes global disruption of alternative splicing and neurodegeneration.Cell. 2012 Jan 20;148(1-2):296-308. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.11.057. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22265417 Free PMC article.
-
Stoichiometries of U2AF35, U2AF65 and U2 snRNP reveal new early spliceosome assembly pathways.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Feb 28;45(4):2051-2067. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw860. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 27683217 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-guided U2AF65 variant improves recognition and splicing of a defective pre-mRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Dec 9;111(49):17420-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1412743111. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25422459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wahl MC, Will CL, Lührmann R. The spliceosome: design principles of a dynamic RNP machine. Cell. 2009;136:701–718. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W, et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409:860–921. - PubMed
-
- Berglund JA, Chua K, Abovich N, Reed R, Rosbash M. The splicing factor BBP interacts specifically with the pre-mRNA branchpoint sequence UACUAAC. Cell. 1997;89:781–787. - PubMed

