Xenopus Kazrin interacts with ARVCF-catenin, spectrin and p190B RhoGAP, and modulates RhoA activity and epithelial integrity
- PMID: 21062899
- PMCID: PMC2987443
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.072041
Xenopus Kazrin interacts with ARVCF-catenin, spectrin and p190B RhoGAP, and modulates RhoA activity and epithelial integrity
Abstract
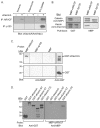
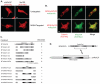
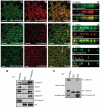
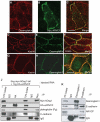
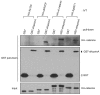
In common with other p120-catenin subfamily members, Xenopus ARVCF (xARVCF) binds cadherin cytoplasmic domains to enhance cadherin metabolic stability or, when dissociated, modulates Rho-family GTPases. We report here that xARVCF binds and is stabilized by Xenopus KazrinA (xKazrinA), a widely expressed conserved protein that bears little homology to established protein families, and which is known to influence keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation and cytoskeletal activity. Although we found that xKazrinA binds directly to xARVCF, we did not resolve xKazrinA within a larger ternary complex with cadherin, nor did it co-precipitate with core desmosomal components. Instead, screening revealed that xKazrinA binds spectrin, suggesting a potential means by which xKazrinA localizes to cell-cell borders. This was supported by the resolution of a ternary biochemical complex of xARVCF-xKazrinA-xβ2-spectrin and, in vivo, by the finding that ectodermal shedding followed depletion of xKazrin in Xenopus embryos, a phenotype partially rescued with exogenous xARVCF. Cell shedding appeared to be the consequence of RhoA activation, and thereby altered actin organization and cadherin function. Indeed, we also revealed that xKazrinA binds p190B RhoGAP, which was likewise capable of rescuing Kazrin depletion. Finally, xKazrinA was found to associate with δ-catenins and p0071-catenins but not with p120-catenin, suggesting that Kazrin interacts selectively with additional members of the p120-catenin subfamily. Taken together, our study supports the essential role of Kazrin in development, and reveals the biochemical and functional association of KazrinA with ARVCF-catenin, spectrin and p190B RhoGAP.
Figures

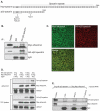
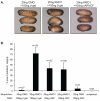
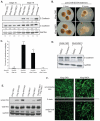
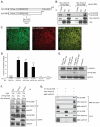
References
-
- Aho S., McLean W. H., Li K., Uitto J. (1998). cDNA cloning, mRNA expression, and chromosomal mapping of human and mouse periplakin genes. Genomics 48, 242-247 - PubMed
-
- Anastasiadis P. Z. (2007). p120-ctn: A nexus for contextual signaling via Rho GTPases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1773, 34-46 - PubMed
-
- Anastasiadis P. Z., Moon S. Y., Thoreson M. A., Mariner D. J., Crawford H. C., Zheng Y., Reynolds A. B. (2000). Inhibition of RhoA by p120 catenin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 637-644 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

