In silico QTL mapping of basal liver iron levels in inbred mouse strains
- PMID: 21062905
- PMCID: PMC3055709
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00025.2010
In silico QTL mapping of basal liver iron levels in inbred mouse strains
Abstract
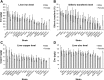
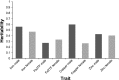
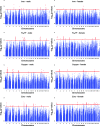
Both iron deficiency and iron excess are detrimental in many organisms, and previous studies in both mice and humans suggest that genetic variation may influence iron status in mammals. However, these genetic factors are not well defined. To address this issue, we measured basal liver iron levels in 18 inbred strains of mice of both sexes on a defined iron diet and found ∼4-fold variation in liver iron in males (lowest 153 μg/g, highest 661 μg/g) and ∼3-fold variation in females (lowest 222 μg/g, highest 658 μg/g). We carried out a genome-wide association mapping to identify haplotypes underlying differences in liver iron and three other related traits (copper and zinc liver levels, and plasma diferric transferrin levels) in a subset of 14 inbred strains for which genotype information was available. We identified two putative quantitative trait loci (QTL) that contain genes with a known role in iron metabolism: Eif2ak1 and Igf2r. We also identified four putative QTL that reside in previously identified iron-related QTL and 22 novel putative QTL. The most promising putative QTL include a 0.22 Mb region on Chromosome 7 and a 0.32 Mb region on Chromosome 11 that both contain only one candidate gene, Adam12 and Gria1, respectively. Identified putative QTL are good candidates for further refinement and subsequent functional studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic analysis reveals polygenic influences on iron, copper, and zinc in mouse hippocampus with neurobiological implications.Hippocampus. 2008;18(4):398-410. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20399. Hippocampus. 2008. PMID: 18189309
-
Quantitative trait loci that determine plasma insulin levels in F2 intercross populations produced from crosses between DDD/Sgn and C57BL/6J inbred mice.J Genet. 2018 Dec;97(5):1413-1420. J Genet. 2018. PMID: 30555089
-
Quantitative genetics of age-related retinal degeneration: a second F1 intercross between the A/J and C57BL/6 strains.Mol Vis. 2007 Jan 25;13:79-85. Mol Vis. 2007. PMID: 17277741 Free PMC article.
-
Giving the Genes a Shuffle: Using Natural Variation to Understand Host Genetic Contributions to Viral Infections.Trends Genet. 2018 Oct;34(10):777-789. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 30131185 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems genetics analysis of iron regulation in the brain.Biochimie. 2009 Oct;91(10):1255-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2009.04.009. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Biochimie. 2009. PMID: 19393285 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In silico QTL mapping of maternal nurturing ability with the mouse diversity panel.Physiol Genomics. 2012 Aug 17;44(16):787-98. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00159.2011. Epub 2012 Jul 3. Physiol Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22759921 Free PMC article.
-
A systems biology approach utilizing a mouse diversity panel identifies genetic differences influencing isoniazid-induced microvesicular steatosis.Toxicol Sci. 2014 Aug 1;140(2):481-92. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu094. Epub 2014 May 20. Toxicol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24848797 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting hemochromatosis: genetic vs. phenotypic manifestations.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Apr;9(8):731. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-5512. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33987429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systems genetic analysis of multivariate response to iron deficiency in mice.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012 Jun;302(11):R1282-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00634.2011. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22461179 Free PMC article.
-
In silico mapping of quantitative trait loci (QTL) regulating the milk ionome in mice identifies a milk iron locus on chromosome 1.Mamm Genome. 2018 Oct;29(9-10):632-655. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9762-7. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Mamm Genome. 2018. PMID: 30073618
References
-
- Adams PC, Reboussin DM, Barton JC, McLaren CE, Eckfeldt JH, McLaren GD, Dawkins FW, Acton RT, Harris EL, Gordeuk VR, Leiendecker-Foster C, Speechley M, Snively BM, Holup JL, Thomson E, Sholinsky P. Hemochromatosis and iron-overload screening in a racially diverse population. N Engl J Med 352: 1769–1778, 2005. - PubMed
-
- Allen KJ, Gurrin LC, Constantine CC, Osborne NJ, Delatycki MB, Nicoll AJ, McLaren CE, Bahlo M, Nisselle AE, Vulpe CD, Anderson GJ, Southey MC, Giles GG, English DR, Hopper JL, Olynyk JK, Powell LW, Gertig DM. Iron-overload-related disease in HFE hereditary hemochromatosis. N Engl J Med 358: 221–230, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GJ. Mechanisms of iron loading and toxicity. Am J Hematol 82: 1128–1131, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

