BH3-only protein Bik is involved in both apoptosis induction and sensitivity to oxidative stress in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 21063407
- PMCID: PMC3008608
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605981
BH3-only protein Bik is involved in both apoptosis induction and sensitivity to oxidative stress in multiple myeloma
Abstract
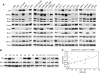
Background: although gene expression profile of multiple myeloma (MM) patients shows a wide range of Bik/Nbk expression, varying from absent to high, its regulation and function in myeloma cells is poorly understood. Thus, we addressed these questions in MM.
Methods: human myeloma cell lines (HMCLs) and primary purified myeloma cells were studied for Bcl-2 family protein expression by western blot and further correlation analysis was performed. Correlative study between Bik and thyrotroph embryonic factor (TEF) transcription factor expression was analysed by PCR. Stress oxidative response was analysed by flow cytometry.
Results: a strong expression of Bik protein was found only in one out of three of HMCL and correlated to Bcl-2 expression (P=0.0006). We demonstrated that Bik could be regulated at the protein level by Bcl-2 and at the transcriptional level by TEF. Bik overexpression sensitises myeloma cells to oxidative stress whereas Bik silencing increases resistance to H(2)O(2) oxidative stress. Furthermore, Bik ectopic expression disrupts Bim/Bcl-2 and Bim/Bcl-xL endogenous complexes triggering Bim release that could induce Bax and Bak activation.
Conclusions: ours results suggest that Bik has a role in both, apoptosis induction and sensitivity to oxidative stress in myeloma cells. Small BH3 mimetic molecules should be considered for further apoptosis-based therapy in myeloma cells expressing endogenous Bik/Bcl-2 complexes.
2010 Cancer Resaerch UK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
BH3-only BIK regulates BAX,BAK-dependent release of Ca2+ from endoplasmic reticulum stores and mitochondrial apoptosis during stress-induced cell death.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 24;280(25):23829-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500800200. Epub 2005 Apr 4. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15809295
-
PAR bZIP-bik is a novel transcriptional pathway that mediates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in fibroblasts.Cell Death Differ. 2009 Jun;16(6):838-46. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.13. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Cell Death Differ. 2009. PMID: 19219069
-
The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib sensitizes cells to killing by death receptor ligand TRAIL via BH3-only proteins Bik and Bim.Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 Mar;4(3):443-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-04-0260. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005. PMID: 15767553
-
BIK, the founding member of the BH3-only family proteins: mechanisms of cell death and role in cancer and pathogenic processes.Oncogene. 2008 Dec;27 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S20-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2009.40. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 19641504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the BH3 (Bcl-2 homology 3) domain in the regulation of apoptosis and Bcl-2-related proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2000 Feb;28(2):51-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0280051. Biochem Soc Trans. 2000. PMID: 10816098 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple myeloma with 1q21 amplification is highly sensitive to MCL-1 targeting.Blood Adv. 2019 Dec 23;3(24):4202-4214. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000702. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31856269 Free PMC article.
-
AT-101 Enhances the Antitumor Activity of Lenalidomide in Patients with Multiple Myeloma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;15(2):477. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020477. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672426 Free PMC article.
-
BIK drives an aggressive breast cancer phenotype through sublethal apoptosis and predicts poor prognosis of ER-positive breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Jun 11;11(6):448. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2654-2. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32528057 Free PMC article.
-
BCL-2 Antagonism to Target the Intrinsic Mitochondrial Pathway of Apoptosis.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;21(22):5021-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0364. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26567361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increase of novel biomarkers for oxidative stress in patients with plasma cell disorders and in multiple myeloma patients with bone lesions.Inflamm Res. 2012 Oct;61(10):1063-7. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0498-7. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Inflamm Res. 2012. PMID: 22674324
References
-
- Avet-Loiseau H, Facon T, Grosbois B, Magrangeas F, Rapp MJ, Harousseau JL, Minvielle S, Bataille R (2002) Oncogenesis of multiple myeloma: 14q32 and 13q chromosomal abnormalities are not randomly distributed, but correlate with natural history, immunological features, and clinical presentation. Blood 99: 2185–2191 - PubMed
-
- Bataille R, Jégo G, Robillard N, Barillé-Nion S, Harousseau JL, Moreau P, Amiot M, Pellat-Deceunynck C (2006) The phenotype of normal, reactive and malignant plasma cells. Identification of ‘many and multiple myelomas’ and of new targets for myeloma therapy. Haematologica 91: 1234–1240 - PubMed
-
- Boyd JM, Gallo GJ, Elangovan B, Houghton AB, Malstrom S, Avery BJ, Ebb RG, Subramanian T, Chittenden T, Lutz RJ, Chinnadurai G (1995) Bik, a novel death-inducing protein shares a distinct sequence motif with Bcl-2 family proteins and interacts with viral and cellular survival-promoting proteins. Oncogene 11: 1921–1928 - PubMed
-
- Castells A, Gusella JF, Ramesh V, Rustgi AK (2000) A region of deletion on chromosome 22q13 is common to human breast and colorectal cancers. Cancer Res 60: 2836–2839 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

