New antiviral therapies for chronic hepatitis C
- PMID: 21063477
- PMCID: PMC2940000
- DOI: 10.1007/s12072-010-9193-3
New antiviral therapies for chronic hepatitis C
Abstract
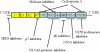
Chronic hepatitis C is an important health issue worldwide. The current standard therapy is based on a combination of pegylated-interferon (pegIFN) and ribavirin (RBV), but this treatment leads to only ~50% sustained virological response (SVR) in patients with HCV genotype 1 and high viral loads, who were mostly null-responders or relapsers. Among HCV genotypes other than HCV genotype 1, especially HCV genotype 4 patients show only 40-70% SVR by this treatment. Although new drugs also depend on the combination of pegIFN and RBV, it appears that these drugs improve not only rapid virological response (RVR) but also early virological response, leading to SVR in these patients. In the near future, we predict higher SVR rates in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with these new drugs.
Keywords: EVR; Polymerase inhibitor; Protease inhibitor; Ribavirin; Vitamin D.
Figures
References
-
- Thomas DL, Seef LB. Natural history of hepatitis C. Clin Liver Dis. 2005;9:383–398. - PubMed
-
- Hoofnagle JH, Seef LB. Peginterferon and ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2444–2451. - PubMed
-
- Marcellin P, Boyer N, Gervais A, Martinot M, Pouteau M, Castelnau C, Kilani A, Areias J, Auperin A, Benhamou JP, Degott C, Eringer S. Long-term histologic improvement and loss of detectable intrahepatic HCV RNA in patients with chronic hepatitis C and sustained response to interferon alpha therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:875–881. - PubMed
-
- Yu JW, Wang GQ, Sun LJ, Li XG, Li SC. Predictive value of rapid virological response and early virological response on sustained virological response in HCV patients treated with pegylated interferon alpha-2a and ribavirin. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:832–836. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

