Regulation of the severity of neuroinflammation and demyelination by TLR-ASK1-p38 pathway
- PMID: 21064192
- PMCID: PMC3377347
- DOI: 10.1002/emmm.201000103
Regulation of the severity of neuroinflammation and demyelination by TLR-ASK1-p38 pathway
Abstract
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) is an evolutionarily conserved mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase kinase which plays important roles in stress and immune responses. Here, we show that ASK1 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), without affecting the proliferation capability of T cells. Moreover, we found that EAE upregulates expression of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in activated astrocytes and microglia, and that TLRs can synergize with ASK1-p38 MAPK signalling in the release of key chemokines from astrocytes. Consequently, oral treatment with a specific small molecular weight inhibitor of ASK1 suppressed EAE-induced autoimmune inflammation in both spinal cords and optic nerves. These results suggest that the TLR-ASK1-p38 pathway in glial cells may serve as a valid therapeutic target for autoimmune demyelinating disorders including multiple sclerosis.
Figures
Clinical evaluation of EAE in wild-type (WT) (n = 13) and ASK1−/− (n = 15) mice during a period of 40 days after MOG immunization.
Proliferative responses of MOG-specific T cells isolated from WT and ASK1−/− mice (n = 4).
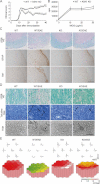
Representative histology of the spinal cords in EAE mice. Lumbar spinal cords were stained with LFB and HE (upper panels) and either an anti-GFAP (middle panels) or anti-iba1 antibody (lower panels). Scale bar: 40 µm for the upper panel and 220 µm for the middle and lower panels.
Representative histology of the optic nerves in EAE mice. Optic nerves were stained with LFB and HE (upper panels) or toluidine blue for the semithin transverse sections (middle panels). The arrows point to the degenerating axons, which were observed further with a transmission electron microscope (TEM; lower panels). Scale bar: 100 µm for the upper panel, 50 µm for the middle panel and 15 µm for the lower panel.
The averaged visual responses from six mice in each group were examined by multifocal electroretinograms. The visual stimulus was applied to seven different areas in the retina. The seven individual traces demonstrate the average responses to the visual stimulus at the corresponding stimulus area (upper panels). Three-dimensional plots show the amplitude variation across the arrays (lower panels). Values are given in nV per square degree (nV/deg2).

Impaired chemokine production in the spinal cords of ASK1−/− EAE mice (n = 4). mRNA expression levels of MCP-1, RANTES and MIP-1α at d40 after MOG immunization were determined using quantitative real-time PCR. GAPDH was used as an internal control. **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05.
Reduced production of TNFα and iNOS in ASK1-deficient microglial cells (n = 4). Cells were stimulated for 16 h with LPS (1 µg/ml) or left unstimulated (NS). TNFα concentrations in the supernatants were determined by ELISA, and iNOS mRNA expression levels were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. *p < 0.05.
TLR3, TLR4 and TLR9 mRNA expression levels in the spinal cord were determined by quantitative real-time PCR analysis (n = 6). ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01.

Representative double-labelling immunohistochemistry for TLR4 or TLR9 with GFAP in the white matter of the spinal cord. Scale bar: 30 µm.
Quantification of the double-stained areas per unit area (0.048 mm2) in (A). The results are expressed as percentages of the wild-type non-EAE (WT) mice (n = 4). **p < 0.001; *p < 0.01.
Representative double-labelling immunohistochemistry for TLR4 or TLR9 with iba1 in the white matter of the spinal cord. Scale bar: 30 µm.
Quantification of the double-stained areas per unit area (0.048 mm2) in (C). The results are expressed as percentages of the wild-type non-EAE (WT) mice (n = 4). **p < 0.001; *p < 0.01.

Effect of ASK1 on TLR ligand-induced p38 activation. Astrocytes derived from WT or ASK1−/− (KO) mice were stimulated with the indicated concentration of the specific TLR ligand for 30 min, followed by immunoblot analysis of total and phosphorylated p38 in cell lysates.
Impaired chemokine production in ASK1-deficient astrocytes (n = 4). Cells were stimulated for 16 h with LPS (10 µg/ml), unmethylated CpG DNA (1 µM) or left unstimulated (NS). Concentrations of MCP-1, RANTES and MIP-1α in culture medium were measured by ELISA. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05.

Medicinal chemistry optimization led to the identification of the compound MSC2032964A.
MSC2032964A showed IC50 values below 10 µM for only two kinases: ASK1 and CK1δ, at 93 and 4800 nM, respectively.


Effect of MSC2032964A on LPS-induced ASK1 activation, as assessed by the phosphorylation of ASK1, p38 and JNK in cultured mouse astrocytes. Confluent astrocytes seeded in 12-well plates were pre-treated with MSC2032964A (10 µM) for 90 min and then treated with LPS (10 µg/ml) for 30 min. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
Clinical evaluation of EAE mice treated with vehicle (n = 7) or MSC2032964A (n = 7) for a period of 40 days after MOG immunization.
Representative histology of the spinal cords and optic nerves of EAE mice treated with vehicle or MSC2032964A. Lumbar spinal cords were stained with LFB and HE (upper panels) and either an anti-GFAP or anti-iba1 antibody (middle panels), and optic nerves were stained with LFB and HE (lower panels). Scale bar: 150 µm for the upper three panels and 20 µm for the lower panel.
Averaged visual response amplitudes from each mouse group (n = 7) were examined by multifocal electroretinograms. *p < 0.05. Values are given in nV per square degree (nV/deg2).

References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B. Inferences, questions and possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature. 2004;430:257–263. - PubMed
-
- Bsibsi M, Persoon-Deen C, Verwer RW, Meeuwsen S, Ravid R, Van Noort JM. Toll-like receptor 3 on adult human astrocytes triggers production of neuroprotective mediators. Glia. 2006;53:688–695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

