The history of the Drosophila TRP channel: the birth of a new channel superfamily
- PMID: 21067449
- PMCID: PMC3103766
- DOI: 10.3109/01677063.2010.514369
The history of the Drosophila TRP channel: the birth of a new channel superfamily
Abstract
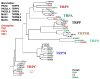
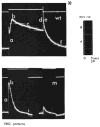
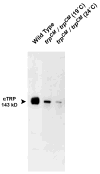
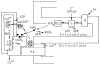
Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are polymodal cellular sensors involved in a wide variety of cellular processes, mainly by changing membrane voltage and increasing cellular Ca(2+). This review outlines in detail the history of the founding member of the TRP family, the Drosophila TRP channel. The field began with a spontaneous mutation in the trp gene that led to a blind mutant during prolonged intense light. It was this mutant that allowed for the discovery of the first TRP channels. A combination of electrophysiological, biochemical, Ca(2+) measurements, and genetic studies in flies and in other invertebrates pointed to TRP as a novel phosphoinositide-regulated and Ca(2+)-permeable channel. The cloning and sequencing of the trp gene provided its molecular identity. These seminal findings led to the isolation of the first mammalian homologues of the Drosophila TRP channels. We now know that TRP channel proteins are conserved through evolution and are found in most organisms, tissues, and cell-types. The TRP channel superfamily is classified into seven related subfamilies: TRPC, TRPM, TRPV, TRPA, TRPP, TRPML, and TRPN. A great deal is known today about participation of TRP channels in many biological processes, including initiation of pain, thermoregulation, salivary fluid secretion, inflammation, cardiovascular regulation, smooth muscle tone, pressure regulation, Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) homeostasis, and lysosomal function. The native Drosophila photoreceptor cells, where the founding member of the TRP channels superfamily was found, is still a useful preparation to study basic features of this remarkable channel.
Figures






References
-
- Acharya JK, Jalink K, Hardy RW, Hartenstein V, Zuker CS. InsP3 receptor is essential for growth and differentiation but not for vision in Drosophila. Neuron. 1997;18(6):881–887. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Irvine RF. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984;312(5992):315–321. - PubMed
-
- Bloomquist BT, Shortridge RD, Schneuwly S, Perdew M, Montell C, Steller H, et al. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988;54:723–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
