Key signaling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer: β-catenin
- PMID: 21067528
- PMCID: PMC3046427
- DOI: 10.1186/bcr2723
Key signaling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer: β-catenin
Abstract
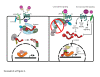
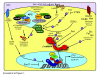
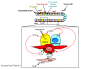
β-Catenin plays important roles in mammary development and tumorigenesis through its functions in cell adhesion, signal transduction and regulation of cell-context-specific gene expression. Studies in mice have highlighted the critical role of β-catenin signaling for stem cell biology at multiple stages of mammary development. Deregulated β-catenin signaling disturbs stem and progenitor cell dynamics and induces mammary tumors in mice. Recent data showing deregulated β-catenin signaling in metaplastic and basal-type tumors suggest a similar link to reactivated developmental pathways and human breast cancer. The present review will discuss β-catenin as a central transducer of numerous signaling pathways and its role in mammary development and breast cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Derksen PW, Liu X, Saridin F, van der Gulden H, Zevenhoven J, Evers B, van Beijnum JR, Griffioen AW, Vink J, Krimpenfort P, Peterse JL, Cardiff RD, Berns A, Jonkers J. Somatic inactivation of E-cadherin and p53 in mice leads to metastatic lobular mammary carcinoma through induction of anoikis resistance and angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2006;10:437–449. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.09.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nagi C, Guttman M, Jaffer S, Qiao R, Keren R, Triana A, Li M, Godbold J, Bleiweiss IJ, Hazan RB. N-cadherin expression in breast cancer: correlation with an aggressive histologic variant - invasive micropapillary carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2005;94:225–235. doi: 10.1007/s10549-005-7727-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

