T-cell epitope prediction and immune complex simulation using molecular dynamics: state of the art and persisting challenges
- PMID: 21067546
- PMCID: PMC2981876
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-7580-6-S2-S4
T-cell epitope prediction and immune complex simulation using molecular dynamics: state of the art and persisting challenges
Abstract
Atomistic Molecular Dynamics provides powerful and flexible tools for the prediction and analysis of molecular and macromolecular systems. Specifically, it provides a means by which we can measure theoretically that which cannot be measured experimentally: the dynamic time-evolution of complex systems comprising atoms and molecules. It is particularly suitable for the simulation and analysis of the otherwise inaccessible details of MHC-peptide interaction and, on a larger scale, the simulation of the immune synapse. Progress has been relatively tentative yet the emergence of truly high-performance computing and the development of coarse-grained simulation now offers us the hope of accurately predicting thermodynamic parameters and of simulating not merely a handful of proteins but larger, longer simulations comprising thousands of protein molecules and the cellular scale structures they form. We exemplify this within the context of immunoinformatics.
Figures
 and
and  are the binding free energies of A and A′ to B, while
are the binding free energies of A and A′ to B, while  and
and  are the free energy differences between the two molecules in their bound and unbound states, respectively. The vertical legs above are ‘alchemical’ paths which transform one molecule into another, while the horizontal legs are ‘chemical’ paths which describe the binding process of one molecule to another.
are the free energy differences between the two molecules in their bound and unbound states, respectively. The vertical legs above are ‘alchemical’ paths which transform one molecule into another, while the horizontal legs are ‘chemical’ paths which describe the binding process of one molecule to another.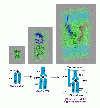


References
-
- Mishra S, Sinha S. Immunoinformatics and modeling perspective of T cell epitope-based cancer immunotherapy: a holistic picture. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2009;27(3):293–306. - PubMed
-
- Flower DR. Immunoinformatics and the in silico prediction of immunogenicity. An introduction. Methods Mol Biol. 2007;409:1–15. full_text. - PubMed
-
- Evans MC. Recent advances in immunoinformatics: application of in silico tools to drug development. Curr Opin Drug Discov Devel. 2008;11(2):233–41. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
