Predominant porB1A and porB1B genotypes and correlation of gene mutations with drug resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in Eastern China
- PMID: 21067570
- PMCID: PMC2992536
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-10-323
Predominant porB1A and porB1B genotypes and correlation of gene mutations with drug resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in Eastern China
Abstract
Background: Variations of porB1A and porB1B genes and their serotypes exist in Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from different geographical areas, and some site mutations in the porB1B gene correlate with drug resistance.
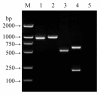
Methods: The β-lactamase production of N. gonorrhoeae isolates was determined by paper acidometric test and nitrocefin discs. The porB1A and porB1B genes of 315 non-penicillinase-producting N. gonorrhoeae (non-PPNG) strains were amplified by PCR for sequencing to determine serotypes and site mutations. A duplex PCR was designed to simultaneously detect both porB1A and porB1B genes. Penicillin and tetracycline resistance was assessed by an in vitro drug sensitivity test.
Results: Of the N. gonorrhoeae isolates, 31.1% tested positive for porB1A and 68.9% for porB1B genes. All the 98 porB1A+ isolates belonging to IA6 serotype with either no mutation at the 120 and 121 sites (88.8%) or a D120G (11.2%) mutation and were no resistance to both penicillin and tetracycline. Among the 217 porB1B+ isolates, 26.7%, 22.6% and 11.5% belonged to IB3, IB3/6 and IB4 serotypes, respectively. Particularly, two novel chimeric serotypes, IB3/6-IB2 and IB2-IB4-IB2, were found in 77 and 8 porB1B+ isolates. Two hundred and twelve (97.7%) of the porB1B+ isolates were presented G120 and/or A121 mutations with 163 (76.9%) at both sites. Interestingly, within the 77 porB1B+ isolates belonging to IB3/6-IB2 serotype, 15 were discovered to possess novel deletions at both A121 and N122 sites. All the replacement mutations at these sites in PorB1B were correlated with resistance and the deletion mutation showed the highest resistance.
Conclusion: N. gonorrhoeae isolates circulating in Eastern China include a sole PorB1A serotype (IA6) and five PorB1B serotypes. Multiple mutations in porB1B genes, including novel A121 and N122 deletions, are correlated with high levels of penicillin and tetracycline resistance.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Correlation between predominant pI genotypes, G120/A121 mutations and drug resistance].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2010 Apr;31(4):442-6. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20513293 Chinese.
-
Plasmid-mediated penicillin and tetracycline resistance among Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in South Africa: prevalence, detection and typing using a novel molecular assay.Sex Transm Dis. 2011 Apr;38(4):329-33. doi: 10.1097/OLQ.0b013e3181fc695a. Sex Transm Dis. 2011. PMID: 21042234
-
The prevalence and epidemiology of plasmid-mediated penicillin and tetracycline resistance among Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates in Guangzhou, China, 2002-2012.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Oct 9;15:412. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1148-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26453557 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time PCR detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae susceptibility to penicillin.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016 Nov;71(11):3090-3095. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw291. Epub 2016 Jul 25. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27494921
-
Clusters of circulating Neisseria gonorrhoeae strains and association with antimicrobial resistance in Shanghai.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008 Mar;61(3):478-87. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm544. Epub 2008 Jan 27. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18227091
Cited by
-
C4BP-IgM protein as a therapeutic approach to treat Neisseria gonorrhoeae infections.JCI Insight. 2019 Dec 5;4(23):e131886. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.131886. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31661468 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of horizontal gene transfer within porB in 19 018 whole-genome Neisseria spp. isolates: a global phylogenetic analysis.Microb Genom. 2023 Jun;9(6):mgen001041. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.001041. Microb Genom. 2023. PMID: 37294009 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmid mediated penicillin and tetracycline resistance among Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolates from Kenya.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Sep 25;20(1):703. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05398-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32977759 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Analysis Reveals Antibiotic-Susceptible Clones and Emerging Resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Saskatchewan, Canada.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020 Aug 20;64(9):e02514-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02514-19. Print 2020 Aug 20. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020. PMID: 32571818 Free PMC article.
-
Computational modeling of cyclotides as antimicrobial agents against Neisseria gonorrhoeae PorB porin protein: integration of docking, immune, and molecular dynamics simulations.Front Chem. 2024 Nov 25;12:1493165. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1493165. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39659871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Global prevalence and incidence of selected curable sexually transmitted infections: overview and estimates. Vol. 2001. Geneva, WHO; pp. 14–19. - PubMed
-
- Workowski KA, Berman SM. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2006;55:1–94. - PubMed
-
- Su X, Jing F, Qimuge, Dia X, Sun H, Ye S. Surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibilities in Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Nanjing, china, 1999-2006. Sex Transm Dis. 2007;34:995–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

