Evolutionary history and molecular epidemiology of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in the Iberian Peninsula and Western Europe
- PMID: 21067589
- PMCID: PMC2992527
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2148-10-347
Evolutionary history and molecular epidemiology of rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus in the Iberian Peninsula and Western Europe
Abstract
Background: Rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus (RHDV) is a highly virulent calicivirus, first described in domestic rabbits in China in 1984. RHDV appears to be a mutant form of a benign virus that existed in Europe long before the first outbreak. In the Iberian Peninsula, the first epidemic in 1988 severely reduced the populations of autochthonous European wild rabbit. To examine the evolutionary history of RHDV in the Iberian Peninsula, we collected virus samples from wild rabbits and sequenced a fragment of the capsid protein gene VP60. These data together with available sequences from other Western European countries, were analyzed following Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo methods to infer their phylogenetic relationships, evolutionary rates and demographic history.
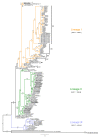
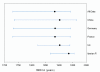
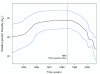
Results: Evolutionary relationships of RHDV revealed three main lineages with significant phylogeographic structure. All lineages seem to have emerged at a common period of time, between ~1875 and ~1976. The Iberian Peninsula showed evidences of genetic isolation, probably due to geographic barriers to gene flow, and was also the region with the youngest MRCA.Overall, demographic analyses showed an initial increase and stabilization of the relative genetic diversity of RHDV, and a subsequent reduction in genetic diversity after the first epidemic breakout in 1984, which is compatible with a decline in effective population size.
Conclusions: Results were consistent with the hypothesis that the current Iberian RHDV arose from a single infection between 1869 and 1955 (95% HPD), and rendered a temporal pattern of appearance and extinction of lineages. We propose that the rising positive selection pressure observed throughout the history of RHDV is likely mediated by the host immune system as a consequence of the genetic changes that rendered the virus virulent. Consequently, this relationship is suggested to condition RHDV demographic history.
Figures
References
-
- Domingo E, Martinez-Salas E, Sobrino F, de la Torre JC, Portela A, Ortin J, Lopez-Galindez C, Perez-Brena P, Villanueva N, Najera R. et al. The quasispecies (extremely heterogeneous) nature of viral RNA genome populations: biological relevance - a review. Gene. 1985;40(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90017-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Biek R, Drummond AJ, Poss M. A virus reveals population structure and recent demographic history of its carnivore host. Science. 2006;24:845–852. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

