Topoisomerase II alpha expression and the benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy for postoperative patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 21067592
- PMCID: PMC2988758
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-621
Topoisomerase II alpha expression and the benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy for postoperative patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Adjuvant chemotherapy has been shown to improve survival rates of postoperative patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Biomarkers could help select an appropriate chemotherapy for NSCLC patients or predict the efficacy of chemotherapy. The objective of this study was to explore the possible prognostic and predictive role of topoisomerase II alpha (TopIIα) expression level in postoperative NSCLC patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy.
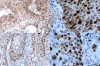
Methods: Patients with stage I-III NSCLC, who underwent surgery in our hospital from January 2004 to December 2007 and who also received adjuvant chemotherapy after surgery, were analyzed in this study. Expression of TopIIα and Ki67 in paraffin-embedded tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The relationships between clinicopathological characteristics, chemotherapy regimens, the expression of biomarkers and disease free survival (DFS) were analyzed.
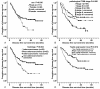
Results: TopIIα and Ki67 were highly expressed in 22.5% and 36.4% of the 151 patients, respectively. Univariate survival analysis showed that male sex (P = 0.036), non-adenocarcinoma (P = 0.004), earlier pathological TNM stage (P = 0.001) or pathological N stage (P < 0.001), and high expression of TopIIα (P = 0.012) were correlated with better DFS, whereas age, smoking history, different chemotherapy regimens, T stage and expression level of Ki67 were of no prognostic significance. Further stratified analysis showed that vinorelbine (NVB)-containing adjuvant regimens were generally associated with better DFS than regimens without NVB in patients with low TopIIα expression, though the difference was not statistically significant (P = 0.065). Pairwise comparisons for patients with low TopIIα expression indicated that the NVB-containing regimen was associated with better DFS than the docetaxel (TXT)-containing regimen (P = 0.047). COX multivariate analysis showed that pathological TNM stage, histological subtype and expression level of TopIIα to be independent of risk factors affecting DFS in postoperative NSCLC patients who received chemotherapy.
Conclusions: High TopIIα expression was discovered to be correlated with better DFS for postoperative NSCLC patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy. The NVB-containing chemotherapy regimen was more effective than the TXT-containing regimen in improving DFS in patients with low TopIIα expression. TopIIα could be considered to be an independent prognostic biomarker of DFS in postoperative NSCLC patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy.
Figures
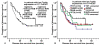
Similar articles
-
[Expression and predictive role of excision repair cross complementation group 1, ribonucleotide reductase subunit M1, and β-tubulin 3 in postoperative patients with non-small cell lung cancer receiving adjuvant chemotherapy].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2010 Aug;32(4):375-82. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2010.04.004. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2010. PMID: 20868593 Chinese.
-
Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is a prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with adjuvant platinum-based chemotherapy.World J Surg Oncol. 2015 Feb 6;13:21. doi: 10.1186/s12957-014-0426-0. World J Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25888998 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of DNA topoisomerases in non-small cell lung cancer and normal lung.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Dec 27;1264(3):337-46. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(95)00171-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995. PMID: 8547322
-
Prognostic value of ERCC1 mRNA expression in non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and gastric cancer in patients from Southern China.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Dec 1;7(12):8312-21. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25674197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Progress of Postoperative Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Stage I Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015 Jun;18(6):374-80. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2015.06.08. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26104895 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive expressional analysis of chemosensitivity-related markers in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Oct;12(20):2666-2679. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14102. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34453496 Free PMC article.
-
6-Methoxy Podophyllotoxin Induces Apoptosis via Inhibition of TUBB3 and TOPIIA Gene Expressions in 5637 and K562 Cancer Cell Lines.Cell J. 2015 Fall;17(3):502-9. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2015.10. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Cell J. 2015. PMID: 26464822 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy following complete resection in NSCLC stages I-IIIA.Eur Respir Rev. 2015 Jun;24(136):340-55. doi: 10.1183/16000617.00005814. Eur Respir Rev. 2015. PMID: 26028645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human topoisomerase II alpha as a prognostic biomarker in cancer chemotherapy.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):47-55. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4270-9. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26482620 Review.
-
Multidrug resistance protein and topoisomerase 2 alpha expression in non-small cell lung cancer are related with brain metastasis postoperatively.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):11537-42. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26617887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, Le Chevalier T, Pignon JP, Vansteenkiste J. International Adjuvant Lung Cancer Trial Collaborative Group. Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:351–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa031644. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, Rigas J, Johnston M, Butts C, Cormier Y, Goss G, Inculet R, Vallieres E, Fry W, Bethune D, Ayoub J, Ding K, Seymour L, Graham B, Tsao MS, Gandara D, Kesler K, Demmy T, Shepherd F. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group; National Cancer Institute of the United States Intergroup JBR.10 Trial Investigators. Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs. observation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2589–2597. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043623. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Rosell R, De Lena M, Carpagnano F, Ramlau R, Gonzáles-Larriba JL, Grodzki T, Pereira JR, Le Groumellec A, Lorusso V, Clary C, Torres AJ, Dahabreh J, Souquet PJ, Astudillo J, Fournel P, Artal-Cortes A, Jassem J, Koubkova L, His P, Riggi M, Hurteloup P. Adjuvant vinorelbine plus cisplatin versus observation in patients with completely resected stage IB-IIIA non-small-cell lung cancer (Adjuvant Navelbine International Trialist Association [ANITA]): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:719–727. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70804-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

