Specificity and rate of human and mouse liver and plasma phosphatidylcholine synthesis analyzed in vivo
- PMID: 21068006
- PMCID: PMC3023562
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.D011916
Specificity and rate of human and mouse liver and plasma phosphatidylcholine synthesis analyzed in vivo
Abstract
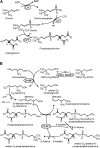
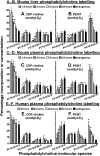
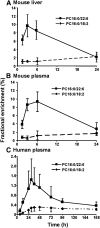
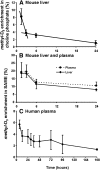
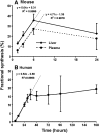
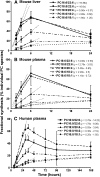
Phosphatidylcholine (PC) synthesis by the direct cytidine diphosphate choline (CDP-choline) pathway in rat liver generates predominantly mono- and di-unsaturated molecular species, while polyunsaturated PC species are synthesized largely by the phosphatidylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase (PEMT) pathway. Although altered PC synthesis has been suggested to contribute to development of hepatocarcinoma and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, analysis of the specificity of hepatic PC metabolism in human patients has been limited by the lack of sensitive and safe methodologies. Here we incorporated a deuterated methyl-D(9)-labled choline chloride, to quantify biosynthesis fluxes through both of the PC synthetic pathways in vivo in human volunteers and compared these fluxes with those in mice. Rates and molecular specificities of label incorporated into mouse liver and plasma PC were very similar and strongly suggest that label incorporation into human plasma PC can provide a direct measure of hepatic PC synthesis in human subjects. Importantly, we demonstrate for the first time that the PEMT pathway in human liver is selective for polyunsaturated PC species, especially those containing docosahexaenoic acid. Finally, we present a multiple isotopomer distribution analysis approach, based on transfer of deuterated methyl groups to S-adenosylmethionine and subsequent sequential methylations of PE, to quantify absolute flux rates through the PEMT pathway that are applicable to studies of liver dysfunction in clinical studies.
Figures


References
-
- Yao Z. M., Vance D. E. 1988. The active synthesis of phosphatidylcholine is required for very low density lipoprotein secretion from rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 263: 2998–3004. - PubMed
-
- Lieber C. S. 2004. New concepts of the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease lead to novel treatments. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 6: 60–65. - PubMed
-
- Zeisel S. H. 1992. Choline: an important nutrient in brain development, liver function and carcinogenesis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 11: 473–481. - PubMed
-
- Van Biervliet S., Van Biervliet G., Van Biervliet J. P., Declercq D., Robberecht E., Christophe A. 2007. Relation between fatty acid composition and clinical status or genotype in cystic fibrosis patients. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 51: 541–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

