Treatment of patients with cardiovascular disease with L-4F, an apo-A1 mimetic, did not improve select biomarkers of HDL function
- PMID: 21068008
- PMCID: PMC3023557
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M011098
Treatment of patients with cardiovascular disease with L-4F, an apo-A1 mimetic, did not improve select biomarkers of HDL function
Abstract
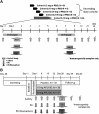
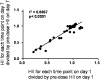
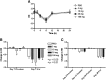
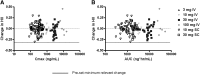
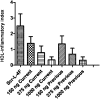
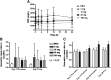
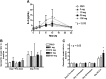
L-4F, an apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) mimetic peptide (also known as APL180), was administered daily by either intravenous (IV) infusion for 7 days or by subcutaneous (SC) injection for 28 days in patients with coronary heart disease in two distinct clinical studies. L-4F was well tolerated at all doses tested. Despite achieving plasma levels (mean maximal plasma concentration of 2,907 ng/ml and 395 ng/ml, following IV infusion and SC injection, respectively), that were effective in previously published animal models, treatment with L-4F, as assessed by biomarkers of HDL function such as HDL-inflammatory index (HII), and paraoxonase activity, did not improve. Paradoxically, there was a 49% increase in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels after seven IV infusions of 30 mg L-4F (P < 0.05; compared with placebo) and a trend for hs-CRP increase in subjects receiving 30 mg SC injection for 28 days. In a subsequent, ex vivo study, addition of L-4F at concentrations of 150, 375, or 1,000 ng/ml to plasma from subjects prior to L-4F treatment resulted in significant dose-dependent HII improvement. In conclusion, in vivo L-4F treatment, delivered by either SC injection or IV infusion, did not improve HDL functional biomarkers despite achieving plasma levels that improved identical biomarkers ex vivo and in animal models.
Figures

References
-
- Gordon T., Castelli W. P., Hjortland M. C., Kannel W. B., Dawber T. R. 1977. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. Am. J. Med. 62: 707–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

