Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies confirms a susceptibility locus for knee osteoarthritis on chromosome 7q22
- PMID: 21068099
- PMCID: PMC3615180
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.132787
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies confirms a susceptibility locus for knee osteoarthritis on chromosome 7q22
Abstract
Objectives: Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent form of arthritis and accounts for substantial morbidity and disability, particularly in older people. It is characterised by changes in joint structure, including degeneration of the articular cartilage, and its aetiology is multifactorial with a strong postulated genetic component.
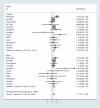
Methods: A meta-analysis was performed of four genome-wide association (GWA) studies of 2371 cases of knee OA and 35 909 controls in Caucasian populations. Replication of the top hits was attempted with data from 10 additional replication datasets.
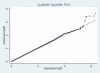
Results: With a cumulative sample size of 6709 cases and 44 439 controls, one genome-wide significant locus was identified on chromosome 7q22 for knee OA (rs4730250, p=9.2 × 10⁻⁹), thereby confirming its role as a susceptibility locus for OA.
Conclusion: The associated signal is located within a large (500 kb) linkage disequilibrium block that contains six genes: PRKAR2B (protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, regulatory, type II, β), HPB1 (HMG-box transcription factor 1), COG5 (component of oligomeric golgi complex 5), GPR22 (G protein-coupled receptor 22), DUS4L (dihydrouridine synthase 4-like) and BCAP29 (B cell receptor-associated protein 29). Gene expression analyses of the (six) genes in primary cells derived from different joint tissues confirmed expression of all the genes in the joint environment.
Figures

References
-
- Zhai G, Hart DJ, Kato BS, MacGregor A, Spector TD. Genetic influence on the progression of radiographic knee osteoarthritis: a longitudinal twin study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007 Feb;15(2):222–225. - PubMed
-
- Valdes AM, Spector TD. The contribution of genes to osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008 Aug;34(3):581–603. - PubMed
-
- Chapman K, Takahashi A, Meulenbelt I, Watson C, Rodriguez-Lopez J, Egli R, et al. A meta-analysis of European and Asian cohorts reveals a global role of a functional SNP in the 5′ UTR of GDF5 with osteoarthritis susceptibility. Hum Mol Genet. 2008 May 15;17(10):1497–1504. - PubMed
-
- Valdes AM, Spector TD, Doherty S, Wheeler M, Hart DJ, Doherty M. Association of the DVWA and GDF5 polymorphisms with osteoarthritis in UK populations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008 Dec 3; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- WT088885/Z/09/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 088785/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 083948/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 068545/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0000934/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 17489/VAC_/Versus Arthritis/United Kingdom
- WT079557MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U122886349/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 18030/ARC_/Arthritis Research UK/United Kingdom
- G0100594/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0901461/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

