Effect of oral snus and medicinal nicotine in smokers on toxicant exposure and withdrawal symptoms: a feasibility study
- PMID: 21068204
- PMCID: PMC3063713
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0349
Effect of oral snus and medicinal nicotine in smokers on toxicant exposure and withdrawal symptoms: a feasibility study
Erratum in
- Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011 May;20(5):1048
Abstract
Background: Smokeless, spitless tobacco products are being introduced and marketed as cigarette substitutes. Data are needed regarding how smokers interested in cessation would use these products, the levels of resultant toxicant exposure, and the feasibility of using these products as aids for tobacco cessation.
Methods: Smokers were randomized to receive Camel Snus (n = 51), Taboka (n = 52), or medicinal nicotine (n = 27) and required to quit smoking for 4 weeks. Measures of toxicant exposure and symptoms of craving and withdrawal were assessed prior to and during product use.
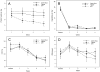
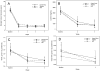
Results: Concentrations of exhaled carbon monoxide, urinary cotinine, urinary 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol and its glucuronides (total NNAL), and urinary N'-nitrosonornicotine and its glucuronide (total NNN) were significantly (P values <0.05) lower at the end of treatment in each group except for total NNN in those receiving Camel Snus (P = 0.066). A significant group × time effect was observed for total NNAL concentrations (P = 0.002) with the decrease greatest in the medicinal nicotine group and smallest decrease in the Camel Snus group. No significant differences between groups were found in craving and withdrawal symptoms.
Conclusions: Enrolling smokers into a cessation study utilizing newer smokeless tobacco products is feasible. Camel Snus and Taboka use was not found to be superior to medicinal nicotine in reducing withdrawal symptoms but decreases in NNAL were smaller in users of Camel Snus.
Impact: This study demonstrates the feasibility of conducting a smoking cessation study utilizing these newer tobacco products. An appropriately powered study is needed to assess smoking cessation rates using these newer products compared with established, safer products such as medicinal nicotine.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00469079.
©2011 AACR.
Figures
References
-
- Russell MA, Jarvis MJ, Feyerabend C. A new age for snuff? Lancet. 1980;1:474–5. - PubMed
-
- Rodu B. An alternative approach to smoking control. Am J Med Sci. 1994;308:32–4. - PubMed
-
- Hatsukami DK, Ebbert JO, Feuer RM, Stepanov I, Hecht SS. Changing smokeless tobacco products new tobacco-delivery systems. Am J Prev Med. 2007;33:S368–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

