Arabidopsis plants deficient in plastidial glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase show alterations in abscisic acid (ABA) signal transduction: interaction between ABA and primary metabolism
- PMID: 21068209
- PMCID: PMC3022406
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erq353
Arabidopsis plants deficient in plastidial glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase show alterations in abscisic acid (ABA) signal transduction: interaction between ABA and primary metabolism
Abstract
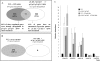
Abscisic acid (ABA) controls plant development and regulates plant responses to environmental stresses. A role for ABA in sugar regulation of plant development has also been well documented although the molecular mechanisms connecting the hormone with sugar signal transduction pathways are not well understood. In this work it is shown that Arabidopsis thaliana mutants deficient in plastidial glycolytic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gapcp1gapcp2) are ABA insensitive in growth, stomatal closure, and germination assays. The ABA levels of gapcp1gapcp2 were normal, suggesting that the ABA signal transduction pathway is impaired in the mutants. ABA modified gapcp1gapcp2 gene expression, but the mutant response to the hormone differed from that observed in wild-type plants. The gene expression of the transcription factor ABI4, involved in both sugar and ABA signalling, was altered in gapcp1gapcp2, suggesting that their ABA insensitivity is mediated, at least partially, through this transcriptional regulator. Serine supplementation was able partly to restore the ABA sensitivity of gapcp1gapcp2, indicating that amino acid homeostasis and/or serine metabolism may also be important determinants in the connections of ABA with primary metabolism. Overall, these studies provide new insights into the links between plant primary metabolism and ABA signalling, and demonstrate the importance of plastidial glycolytic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in these interactions.
Figures


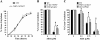
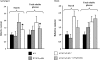



References
-
- Acevedo-Hernandez GJ, Leon P, Herrera-Estrella LR. Sugar and ABA responsiveness of a minimal RBCS light-responsive unit is mediated by direct binding of ABI4. The Plant Journal. 2005;43:506–519. - PubMed
-
- Akihiro T, Mizuno K, Fujimura T. Gene expression of ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and starch contents in rice cultured cells are cooperatively regulated by sucrose and ABA. Plant and Cell Physiology. 2005;46:937–946. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

