HIV-1 load comparison using four commercial real-time assays
- PMID: 21068276
- PMCID: PMC3020484
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01688-10
HIV-1 load comparison using four commercial real-time assays
Abstract
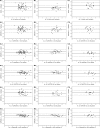
The HIV-1 RNA viral load is commonly used for the monitoring of disease progression and antiretroviral treatment of HIV-1-infected patients. Since the misestimating of values could lead to inappropriate therapeutical management, the comparative performances, especially the ability to span the genetic diversity of HIV-1, of available automated real-time assays need to be evaluated. We conducted a prospective study with 74 consenting patients enrolled between March 2007 and November 2008. A blood sample was obtained at the time of diagnosis of HIV seropositivity and blindly tested for HIV-1 RNA by at least 4 commercial tests: the Abbott m2000 RealTime HIV-1, bioMérieux NucliSens EasyQ HIV-1, version 1.2 (v1.2), and Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan (CAP/CTM) v1.0 and v2.0 assays. The means of difference were null between CAP/CTM v2.0 and Abbott for CRF02_AG subtypes but positive in favor of CAP/CTM v2.0 for genotype B and negative in favor of NucliSens for all genotypes. The standard deviation (SD) of difference ranged from 0.3 to 0.59, depending on the considered couples of assays. Reliabilities of these four tests, appreciated by the standard deviation of difference between the measurement and the estimated "true" viral load and by the coefficient of reliability, were significantly different (P < 10(-4)) among each other. Significant differences were also observed within each group of HIV-1 genotype. The global disparity was higher for CRF02_AG than for B subtypes. This study indicates a risk of viral load misestimating or discrepancies between techniques, depending on the HIV-1 subtype, and speaks in favor of using the same assay for the monitoring of HIV-1-infected patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison between the automated Roche Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan HIV-1 test version 2.0 assay and its version 1 and Nuclisens HIV-1 EasyQ version 2.0 assays when measuring diverse HIV-1 genotypes in China.J Clin Virol. 2012 Jan;53(1):33-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2011.10.001. Epub 2011 Nov 2. J Clin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22051503
-
Performance of NucliSens HIV-1 EasyQ Version 2.0 compared with six commercially available quantitative nucleic acid assays for detection of HIV-1 in China.Mol Diagn Ther. 2010 Oct 1;14(5):305-16. doi: 10.1007/BF03256386. Mol Diagn Ther. 2010. PMID: 21053996
-
Evaluation of the Abbott m2000 RealTime human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) assay for HIV load monitoring in South Africa compared to the Roche Cobas AmpliPrep-Cobas Amplicor, Roche Cobas AmpliPrep-Cobas TaqMan HIV-1, and BioMerieux NucliSENS EasyQ HIV-1 assays.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Jul;47(7):2209-17. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01761-08. Epub 2009 May 6. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19420172 Free PMC article.
-
Performance evaluation of the new Roche Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan HIV-1 test version 2.0 for quantification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2010 Apr;48(4):1195-200. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01832-09. Epub 2010 Feb 17. J Clin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20164281 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative performance of the Biocentric Generic Viral Load, Roche CAP/CTM v1.5, Roche CAP/CTM v2.0 and m2000 Abbott assays for quantifying HIV-1 B and non-B strains: Underestimation of some CRF02 strains.J Clin Virol. 2019 Jan;110:36-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2018.12.002. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Clin Virol. 2019. PMID: 30530097
Cited by
-
Ability of two commercially available assays (Abbott RealTime HIV-1 and Roche Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan HIV-1 Version 2.0) to quantify low HIV-1 RNA Levels (<1,000 copies/milliliter): comparison with clinical samples and NIBSC working reagent for nucleic acid testing assays.J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Jun;52(6):2019-26. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00288-14. Epub 2014 Mar 26. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24671791 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative performances of HIV-1 RNA load assays at low viral load levels: results of an international collaboration.J Clin Microbiol. 2014 Feb;52(2):517-23. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02461-13. Epub 2013 Dec 4. J Clin Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24478482 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of HIV-1 viral load assay performance in immunological stable patients with low or undetectable viremia.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2013 Feb;202(1):67-75. doi: 10.1007/s00430-012-0249-y. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 22699843
-
Analytical Performances of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 RNA-Based Amplix® Real-Time PCR Platform for HIV-1 RNA Quantification.AIDS Res Treat. 2016;2016:7954810. doi: 10.1155/2016/7954810. Epub 2016 Dec 5. AIDS Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 28050283 Free PMC article.
-
ViraLite: An Ultracompact HIV Viral Load Self-Testing System with Internal Quality Control.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 3:2025.04.01.25325036. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.01.25325036. medRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40236396 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Altman, D. G., and J. M. Bland. 1983. Measurement in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician 32:307-317.
-
- Damond, F., B. Roquebert, A. Benard, G. Collin, M. Miceli, P. Yeni, F. Brun-Vezinet, and D. Descamps. 2007. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) plasma load discrepancies between the Roche COBAS AMPLICOR HIV-1 MONITOR version 1.5 and the Roche COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan HIV-1 assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 45:3436-3438. - PMC - PubMed
-
- De Bel, A., D. Marissens, L. Debaisieux, C. Liesnard, S. Van den Winjngaert, S. Lauwers, and D. Piérard. 2010. Correction of underquantification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 load with the second version of the Roche Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 48:1337-1342. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Mendoza, C., M. Koppelman, B. Montes, V. Ferre, V. Soriano, H. Cuypers, M. Segondy, and T. Oosterlaken. 2005. Multicenter evaluation of the NucliSens EasyQ HIV-1 v1.1 assay for the quantitative detection of HIV-1 RNA in plasma. J. Virol. Methods 127:54-57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

