Prevalence and characterization of human Shigella infections in Henan Province, China, in 2006
- PMID: 21068291
- PMCID: PMC3020427
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01508-10
Prevalence and characterization of human Shigella infections in Henan Province, China, in 2006
Abstract
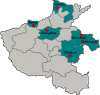
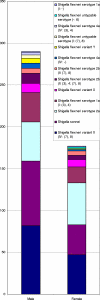
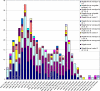
In 2006, 3,531 fecal samples were collected from patients with diarrhea in Henan Province, China. A total of 467 (13.2%) Shigella strains were isolated and serotyped. Seventy-one Shigella flexneri strains were characterized by MIC determination, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), and detection of genes encoding cephalosporin resistance. Most infections were caused by S. flexneri variant X [IV:(7),8] (27.6%), S. sonnei (24.2%), and S. flexneri 2a (20.8%). However, large regional differences were observed. Significantly higher odds (2.0) of females compared to males were infected with S. flexneri 2a. Untypeable S. flexneri (-:6) isolates were absent among males, as were untypeable S. flexneri [I:(7),8] isolates among females. Patient ages ranged from 2 months to 82 years, with 231 subjects (49.7%) <5 years of age. Most of the patients were male (62.1% [n = 290]). Infections peaked in July; week 27 with 38 cases (8.1%). All of the 71 S. flexneri conferred resistance to nalidixic acid; in addition, 21% (n = 15) and 79% (n = 56) were high- and low-level resistant to ciprofloxacin, respectively. Six S. flexneri isolates {serotype 2b [II:7,(8)] and 2b [II:(3),4;7,(8)]} harbored the bla(CTX-M-14) or bla(CTX-M-15) gene. A total of 52 unique XbaI PFGE patterns were observed among the 71 S. flexneri isolates with 11 distinct PFGE clusters. This study revealed a high prevalence of shigellosis with geographical differences in the distribution of serotypes in the distribution of serotypes and also differences in comparisons by gender. A high frequency of resistance, including 100% resistance to ciprofloxacin and resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins, was observed. We detected several isolates exhibiting the same PFGE type and MIC profile, indicating multiple undetected outbreaks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial-resistant Shigella infections from Iran: an overlooked problem?J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 May;67(5):1128-33. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks023. Epub 2012 Feb 17. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22345385
-
Characterization of fluoroquinolone-resistant Shigella flexneri in Hangzhou area of China.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009 May;63(5):917-20. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp087. Epub 2009 Mar 18. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009. PMID: 19297378
-
The rise in domestic shigellosis and the genomic characteristics of Shigella clones linked to men who have sex with men in Taiwan, 2015‒2022.Microbiol Spectr. 2025 Apr;13(4):e0229024. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02290-24. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Microbiol Spectr. 2025. PMID: 39945556 Free PMC article.
-
Keratitis due to Shigella flexneri.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Jun;44(6):2291-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00481-06. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16757643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Shigella sonnei: A highly drug-resistant pathogen of increasing prevalence.Virulence. 2023 Dec;14(1):2280838. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2023.2280838. Epub 2023 Nov 23. Virulence. 2023. PMID: 37994877 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Characterization of Multidrug-Resistant Shigella flexneri.Cureus. 2024 Jan 31;16(1):e53276. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53276. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38435906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotype distribution and characteristics of antimicrobial resistance in Shigella isolated from Henan province, China, 2001-2008.Epidemiol Infect. 2013 Sep;141(9):1946-52. doi: 10.1017/S0950268812002543. Epub 2012 Nov 14. Epidemiol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23151414 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance and genetic characterization of Shigella spp. in Shanxi Province, China, during 2006-2016.BMC Microbiol. 2019 May 29;19(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12866-019-1495-6. BMC Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31142259 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial agents and antibiotic resistance profiles of infections from different sites that occurred among patients at Debre Markos Referral Hospital, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.BMC Res Notes. 2017 Jul 6;10(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2584-y. BMC Res Notes. 2017. PMID: 28683780 Free PMC article.
-
A review on Sero diversity and antimicrobial resistance patterns of Shigella species in Africa, Asia and South America, 2001-2014.BMC Res Notes. 2016 Aug 30;9(1):422. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-2236-7. BMC Res Notes. 2016. PMID: 27576729 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andres, P., A. Petroni, D. Faccone, F. Pasteran, R. Melano, M. Rapoport, M. Martinez, C. Culasso, B. A. Di, B. Irigoyen, J. Mulki, A. Procopio, S. M. von, and M. Galas. 2005. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in Shigella flexneri from Argentina: first report of TOHO-1 outside Japan. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 25:501-507. - PubMed
-
- Bangtrakulnonth, A., A. R. Vieira, D. M. Lo Fo Wong, S. Pornreongwong, C. Pulsrikarn, P. Sawanpanyalert, R. S. Hendriksen, and F. M. Aarestrup. 2008. Shigella from humans in Thailand during 1993 to 2006: spatial-time trends in species and serotype distribution. Foodborne. Pathog. Dis. 5:773-784. - PubMed
-
- Bennish, M. L., and B. J. Wojtyniak. 1991. Mortality due to shigellosis: community and hospital data. Rev. Infect. Dis. 13(Suppl. 4):S245-S251. - PubMed
-
- Bopp, C. A., F. W. Brenner, P. I. Fields, J. G. Wells, and N. A. Strockbine. 2003. Escherichia, Shigella, and Salmonella, p. 654-671. In P. R. Murray, E. J. Baron, J. H. Jorgensen, M. A. Pfaller, and R. H. Yolken (ed.), Manual of clinical microbiology, 8th ed. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
-
- Collignon, P., J. H. Powers, T. M. Chiller, A. Kidara-Kane, and F. M. Aarestrup. 2009. World Health Organization ranking of antimicrobials according to their importance in human medicine: a critical step for developing risk management strategies for the use of antimicrobials in food production animals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 49:132-141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

