The 32-year relationship between cholesterol and dementia from midlife to late life
- PMID: 21068429
- PMCID: PMC2995387
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181feb2bf
The 32-year relationship between cholesterol and dementia from midlife to late life
Abstract
Background: Cellular and animal studies suggest that hypercholesterolemia contributes to Alzheimer disease (AD). However, the relationship between cholesterol and dementia at the population level is less clear and may vary over the lifespan.
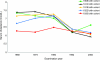
Methods: The Prospective Population Study of Women, consisting of 1,462 women without dementia aged 38-60 years, was initiated in 1968-1969 in Gothenburg, Sweden. Follow-ups were conducted in 1974-1975, 1980-1981, 1992-1993, and 2000-2001. All-cause dementia was diagnosed according to DSM-III-R criteria and AD according to National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke-Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association criteria. Cox proportional hazards regression examined baseline, time-dependent, and change in cholesterol levels in relation to incident dementia and AD among all participants. Analyses were repeated among participants who survived to the age of 70 years or older and participated in the 2000-2001 examination.
Results: Higher cholesterol level in 1968 was not associated with an increased risk of AD (highest vs lowest quartile: hazard ratio [HR] 2.82, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.94-8.43) among those who survived to and participated in the 2000-2001 examination. While there was no association between cholesterol level and dementia when considering all participants over 32 years, a time-dependent decrease in cholesterol over the follow-up was associated with an increased risk of dementia (HR 2.35, 95% CI 1.22-4.58).
Conclusion: These data suggest that midlife cholesterol level is not associated with an increased risk of AD. However, there may be a slight risk among those surviving to an age at risk for dementia. Declining cholesterol levels from midlife to late life may better predict AD risk than levels obtained at one timepoint prior to dementia onset. Analytic strategies examining this and other risk factors across the lifespan may affect interpretation of results.
Figures
Comment in
-
Midlife cholesterol level and dementia 32 years later: is there a risk?Neurology. 2010 Nov 23;75(21):1862-3. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181feb315. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Neurology. 2010. PMID: 21068424 No abstract available.
References
-
- Refolo LM, Malester B, LaFrancois J, et al. Hypercholesterolemia accelerates the Alzheimer's amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 2000;7:321–331. - PubMed
-
- Sparks DL, Scheff SW, Hunsaker JC 3rd, Liu H, Landers T, Gross DR. Induction of Alzheimer-like beta-amyloid immunoreactivity in the brains of rabbits with dietary cholesterol. Exp Neurol 1994;126:88–94. - PubMed
-
- Refolo LM, Pappolla MA, LaFrancois J, et al. A cholesterol-lowering drug reduces beta-amyloid pathology in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2001;8:890–899. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 5R03AG026098/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37DA011796/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- 1R03AG026098-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37AA12303/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH 42243/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1R21AG028754/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH079240/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH076953/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083738-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG028754/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS060271-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS06027-01/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- K99MH086049-01A1/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG21136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH072866-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases