Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow
- PMID: 21068832
- PMCID: PMC3206737
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09613
Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow
Abstract
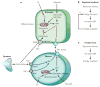
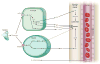
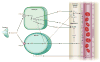
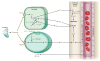
Blood flow in the brain is regulated by neurons and astrocytes. Knowledge of how these cells control blood flow is crucial for understanding how neural computation is powered, for interpreting functional imaging scans of brains, and for developing treatments for neurological disorders. It is now recognized that neurotransmitter-mediated signalling has a key role in regulating cerebral blood flow, that much of this control is mediated by astrocytes, that oxygen modulates blood flow regulation, and that blood flow may be controlled by capillaries as well as by arterioles. These conceptual shifts in our understanding of cerebral blood flow control have important implications for the development of new therapeutic approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Attwell D, Laughlin SB. An energy budget for signaling in the grey matter of the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2001;21:1133–1145. - PubMed
-
- Leffler CW, Busija DW, Mirro R, Armstead WM, Beasley DG. Effects of ischemia on brain blood flow and oxygen consumption of newborn pigs. Am J Physiol. 1989;257:H1917–H1926. - PubMed
-
- Girouard H, Iadecola C. Neurovascular coupling in the normal brain and in hypertension, stroke, and Alzheimer disease. J Appl Physiol. 2006;100:328–335. - PubMed
-
- Baptiste DC, Fehlings M. Pharmacological approaches to repair the injured spinal cord. J Neurotrauma. 2006;23:318–334. - PubMed
-
- Tian R, et al. Role of extracellular and intracellular acidosis for hypercapnia-induced inhibition of tension of isolated rat cerebral arteries. Circ Res. 1995;76:269–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

