Prone or PEEP, PEEP and prone
- PMID: 21069288
- PMCID: PMC3028103
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-010-2070-7
Prone or PEEP, PEEP and prone
Figures
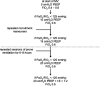
Comment on
-
Prone ventilation reduces mortality in patients with acute respiratory failure and severe hypoxemia: systematic review and meta-analysis.Intensive Care Med. 2010 Apr;36(4):585-99. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1748-1. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Intensive Care Med. 2010. PMID: 20130832
References
-
- Sud S, Friedrich JO, Taccone P, Polli F, Adhikari NK, Latini R, Pesenti A, Guerin C, Mancebo J, Curley MA, Fernandez R, Chan MC, Beuret P, Voggenreiter G, Sud M, Tognoni G, Gattinoni L. Prone ventilation reduces mortality in patients with acute respiratory failure and severe hypoxemia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Med. 2010;36:585–599. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1748-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Taccone P, Pesenti A, Latini R, Polli F, Vagginelli F, Mietto C, Caspani L, Raimondi F, Bordone G, Iapichino G, Mancebo J, Guérin C, Ayzac L, Blanch L, Fumagalli R, Tognoni G, Gattinoni L, Prone-Supine II Study Group Prone positioning in patients with moderate and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;302:1977–1984. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1614. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murray JF, Matthay MA, Luce JM, Flick MR. An expanded definition of the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988;138:720–723. - PubMed
-
- Ortiz RM, Cilley RE, Bartlett RH. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in pediatric respiratory failure. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1987;34:39–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

