Cell-specific and hypoxia-dependent regulation of human HIF-3α: inhibition of the expression of HIF target genes in vascular cells
- PMID: 21069422
- PMCID: PMC11115058
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0575-4
Cell-specific and hypoxia-dependent regulation of human HIF-3α: inhibition of the expression of HIF target genes in vascular cells
Abstract
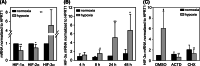
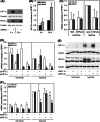
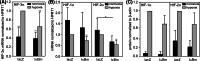
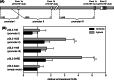
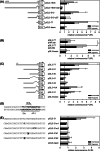
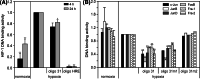
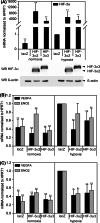
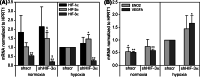
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF) are transcription factors responding to reduced oxygen levels and are of utmost importance for regulation of a widespread of cellular processes, e.g., angiogenesis. In contrast to HIF-1α/HIF-2α, the relevance of HIF-3α for the regulation of the HIF pathway in human vascular cells is largely unknown. HIF-3α mRNA increases under hypoxia in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. Analysis of HIF-3α isoforms revealed a cell type-specific pattern, but only one isoform, HIF-3α2, is hypoxia-inducible. Reporter gene assays of the appropriate promoter localized a 31-bp fragment, mediating this hypoxic regulation. The contribution of HIF-1/2 and NFκB to the HIF-3α induction was verified. Functional studies focused on overexpression of HIF-3α isoforms, which decrease the hypoxia-mediated expression of VEGFA and Enolase2. These data support the notion of a hypoxia-induced inhibitory function of HIF-3α and demonstrate for the first time the existence of this negative regulation of HIF-signaling in vascular cells.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Sluimer JC, Gasc JM, van Wanroij JL, Kisters N, Groeneweg M, Sollewijn G, Cleutjens JP, van den Akker LH, Corvol P, Wouters BG, Daemen MJ, Bijnens AP. Hypoxia, hypoxia-inducible transcription factor, and macrophages in human atherosclerotic plaques are correlated with intraplaque angiogenesis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:1258–1265. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.12.025. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

