Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia
- PMID: 21069663
- PMCID: PMC7061250
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000025.pub2
Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia
Abstract
Background: Eclampsia, the occurrence of a seizure (fit) in association with pre-eclampsia, is rare but potentially life-threatening. Magnesium sulphate is the drug of choice for treating eclampsia. This review assesses its use for preventing eclampsia.
Objectives: To assess the effects of magnesium sulphate, and other anticonvulsants, for prevention of eclampsia.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group's Trials Register (4 June 2010), and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials Register (The Cochrane Library 2010, Issue 3).
Selection criteria: Randomised trials comparing anticonvulsants with placebo or no anticonvulsant, or comparisons of different drugs, for pre-eclampsia.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors assessed trial quality and extracted data independently.
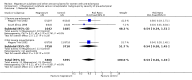
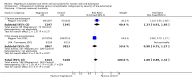
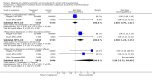
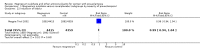
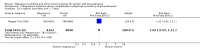
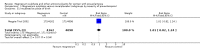
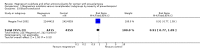
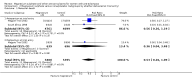
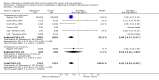
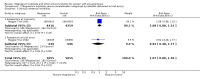
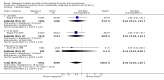
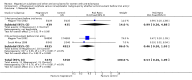
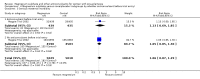
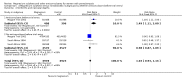
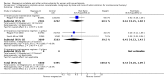
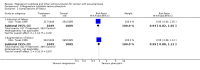
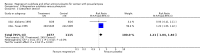
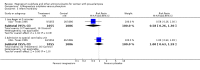
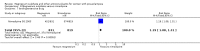
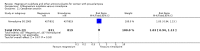
Main results: We included 15 trials. Six (11,444 women) compared magnesium sulphate with placebo or no anticonvulsant: magnesium sulphate more than a halved the risk of eclampsia (risk ratio (RR) 0.41, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.29 to 0.58; number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) 100, 95% CI 50 to 100), with a non-significant reduction in maternal death (RR 0.54, 95% CI 0.26 to 1.10) but no clear difference in serious maternal morbidity (RR 1.08, 95% CI 0.89 to 1.32). It reduced the risk of placental abruption (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.83; NNTB 100, 95% CI 50 to 1000), and increased caesarean section (RR 1.05, 95% CI 1.01 to 1.10). There was no clear difference in stillbirth or neonatal death (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.93 to 1.15). Side effects, primarily flushing, were more common with magnesium sulphate (24% versus 5%; RR 5.26, 95% CI 4.59 to 6.03; number need to treat for an additional harmful outcome (NNTH) 6, 95% CI 5 to 6).Follow-up was reported by one trial comparing magnesium sulphate with placebo: for 3375 women there was no clear difference in death (RR 1.79, 95% CI 0.71 to 4.53) or morbidity potentially related to pre-eclampsia (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.26) (median follow-up 26 months); for 3283 children exposed in utero there was no clear difference in death (RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.57 to 1.84) or neurosensory disability (RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.38 to 1.58) at age 18 months.Magnesium sulphate reduced eclampsia compared to phenytoin (three trials, 2291 women; RR 0.08, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.60) and nimodipine (one trial, 1650 women; RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.14 to 0.77).
Authors' conclusions: Magnesium sulphate more than halves the risk of eclampsia, and probably reduces maternal death. There is no clear effect on outcome after discharge from hospital. A quarter of women report side effects with magnesium sulphate.
Conflict of interest statement
Lelia Duley is a principal investigator for the Magpie Trial, which compared magnesium sulphate with placebo and was, therefore, not involved in the assessment or data extraction of this trial.
Figures

























































Update of
-
Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(2):CD000025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000025. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD000025. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000025.pub2. PMID: 12804383 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Denmark 2000 {published data only}
-
- Rudnicki M, Frolich A, Pilsgaard K, Nyrnberg L, Moller M, Sanchez M, et al. Comparison of magnesium and methyldopa for the control of blood pressure in pregnancies complicated with hypertension. Gynecologic and Obstetric Investigation 2000;49:231‐5. - PubMed
India 2008 {published data only}
-
- Sharma R, Mir S, Rizvi M, Akthar S. Efficacy of magnesium sulphate versus phenytoin in seizure control and prophylaxis in patients of eclampsia and severe pre‐eclampsia. JK Science 2008;10(4):181‐5.
Magpie Trial 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Bricker L, Magpie Trial Collaborative Group. The Magpie Trial: magnesium sulphate versus placebo for women with pre‐eclampsia. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics and Gynecology; 2000 Sept 3‐8; Washington DC, USA. 2000:47.
-
- Duley L, Campbell L. The Magpie Trial: magnesium sulphate for pre‐eclampsia, evaluating the effects on women and their babies. MIDIRS Midwifery Digest 1999;9:48‐51.
-
- Duley L, Magpie Trial Collaborative Group. The Magpie Trial: magnesium sulphate versus placebo for women with pre‐eclampsia. Hypertension in Pregnancy 2000;19(Suppl 1):63.
Malaysia 1994 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Adeeb N, Hatta AZ, Shariff J. Comparing magnesium sulphate to diazepam in managing severe pre‐eclampsia and eclampsia. 10th World Congress of the International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy; 1996 August 4‐8; Seattle, Washington, USA. 1996:246.
-
- Adeeb N, Ho CM. Comparing magnesium sulphate versus diazepam in the management of severe pre‐eclampsia and eclampsia. 9th International Congress of the International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy; 1994 March 15‐18; Sydney, Australia. 1994:38.
Mexico 1992 {published data only}
-
- Walss Rodriguez RJ, Levario AR. Anticonvulsant treatment of severe pre‐eclampsia: comparison of diazepam and magnesium sulfate. Ginecologia y Obstetricia de Mexico 1992;60:331‐5. - PubMed
Mexico 1998 {published data only}
-
- Vargas AG, Salmeron PI, Sanchez GAR, Jiminez AL, Rubio GAF. Efficancy of isosorbide in aerosol in the management of hypertensive crisis of severe preeclampsia [Eficacia del isosorbide en aerosol en el manejo de la crisis hipertensiva de la preeclampsia]. Ginecologia y Obstetricia De Mexico 1998;66:316‐9. - PubMed
Nimodipine SG 2003 {published data only}
-
- Belfort M, Anthony J, Saade G, Nimodipine Study Group. Interim report of the nimodipine vs. magnesium sulfate for seizure prophylaxis in severe preeclampsia study: an international randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1998;178(1 Pt 2):S7.
-
- Belfort M, Saade G, Yared M, Abedejos P, Dorman K. Change in estimated cerebral perfusion pressure following nimodipine or magnesium sulfate in patients with severe preeclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1998;178:S114. - PubMed
-
- Belfort MA, Anthony J, Saade GR, Allen JC, for the Nimodipine Study Group. A comparison of magnesium sulfate and nimodipine for the prevention of eclampsia. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;348:304‐11. - PubMed
-
- Belfort MA, Saade GR, Yared M, Grunewald C, Herd A, Varner MA, et al. Change in estimated cerebral perfusion pressure after treatment with nimodipine or magnesium sulfate in patients with pre‐eclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1999;181:402‐7. - PubMed
-
- Hollenberg NK. A comparison of magnesium sulfate and nimodipine for the prevention of eclampsia. Current Hypertension Reports 2003;5(4):288‐9. - PubMed
South Africa 1994 {published data only}
-
- Moodley J, Moodley J. Prophylactic anticonvulsant therapy in hypertensive crises of pregnancy ‐ the need for a large randomized trial. Hypertension in Pregnancy 1994;13:245‐52.
South Africa 1998 {published data only}
-
- Anthony J, Rush R. A randomised controlled trial of intravenous magnesium sulphate versus placebo. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1998;105:809‐10. - PubMed
-
- Coetzee E, Dommisse J, Anthony J. A randomised controlled trial of intravenous magnesium sulphate versus placebo in the management of women with severe pre‐eclampsia. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1998;105:300‐3. - PubMed
-
- Coetzee E, Dommisse J, Anthony J. Are anticonvulsants necessary in the management of severe gestational proteinuric hypertension. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 1994;46:121.
-
- Coetzee E, Dommisse J, Anthony J. The prediction and prevention of seizures in 571 patients with severe pre‐eclampsia. 10th World Congress of the International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy; 1996 August 4‐8; Seattle, Washington, USA, 1996:124. Seattle, 1996:124.
-
- Coetzee EJ, Anthony J, Dommisse AJ. Does magnesium sulphate prevent eclampsia in severe gestational proteinuria hypertension. Prenatal and Neonatal Medicine 1996;1(Suppl 1):9.
Taiwan 1995 {published data only}
-
- Chen FP, Chang SD, Chu KK. Expectant management in severe preeclampsia: does magnesium sulfate prevent the development of eclampsia. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1995;74:181‐5. - PubMed
USA ‐ Alabama 1995 {published data only}
-
- Atkinson MW, Guinn D, Owen J, Hauth JC. Does magnesium sulfate affect the length of labor induction in women with pregnancy‐associated hypertension?. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1995;173:1219‐22. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson MW, Guinn D, Owen J, Hauth JC. Does magnesium sulfate prolong labor induction in women with gestational hypertension?. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1995;172:384. - PubMed
USA ‐ Maryland 1993 {published data only}
-
- Friedman SA, Lim KH, Baker C, Repke JT. Phenytoin vs magnesium sulfate in preeclampsia: a pilot study. American Journal of Perinatology 1993;10:233‐8. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SA, Lim KH, Baker CA, Repke JT. A comparison of phenytoin infusion versus magnesium sulphate infusion in preeclampsia. Proceedings of the 10th Annual Meeting of the Society of Perinatal Obstetricians; 1990 Jan 23‐27; Houston, Texas, USA. 1990:16.
-
- Repke JT, Friedman SA, Lim KH, Baker CA. Magnesium sulfate vs phenytoin in preeclampsia: preliminary results from a randomized clinical trial. Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of the Society of Perinatal Obstetricians; 1989 Feb 1‐4; New Orleans, Louisiana, USA. 1989:123.
USA ‐ Memphis 1997 {published data only}
-
- Witlin A, Friedman S, Sibai B. The effect of magnesium sulfate therapy on the duration of labor in women with mild preeclampsia at term: a randomized double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1997;176(1 Pt 2):S15. - PubMed
-
- Witlin AG, Friedman SA, Sibai BM. The effect of magnesium sulfate therapy on the duration of labor in women with mild preeclampsia at term: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1997;76:623‐7. - PubMed
USA ‐ Tennessee 2001 {published data only}
-
- Livingston J, Livingston L, Mabie B, Sibai B. The efficacy of magnesium sulfate in women with mild preeclampsia: a double blinded placebo controlled trial. Hypertension in Pregnancy 2002;20(Suppl 1):42.
-
- Livingston J, Livingston L, Ramsey R, Kao L, Mabie B, Sibai B. Magnesium sulfate in women with mild preeclampsia: a double blind placebo controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2001;185(Suppl 6):S75.
-
- Livingston JC, Livingston LW, Ramsey R, Mabie BC, Sibai BM. Magnesium sulfate in women with mild preeclampsia: a randomised controlled trial. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;101(2):217‐20. - PubMed
USA ‐ Texas 1995 {published data only}
-
- Leveno KJ, Alexander JM, McIntire DD, Lucas MJ. Does magnesium sulfate given for the prevention of eclampsia affect the outcome of labor?. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1998;178:707‐12. - PubMed
-
- Lucas MJ, Leveno KJ, Cunningham MD. A comparison of magnesium sulfate with phenytoin for the prevention of eclampsia. New England Journal of Medicine 1995;333:201‐5. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbade 2006 {published data only}
-
- Abbade JF, Costa RAA, Martins AMVC, Rudge MVC, Peracoli JC. Zuspan's scheme versus alternative scheme of magnesium sulphate to prevent or to treat eclampsia: comparison of magnesium serum concentrations. Hypertension in Pregnancy 2006;25(Suppl 1):152.
Antartani 2006 {published data only}
-
- Antartani RC, Kiran A. A comparative study of magnesium sulfate vs phenytoin for prevention of recurrence of seizures in eclampsia. 49th All India Congress of Obstetrics and Gynaecology; 2006 Jan 6‐9; Cochin, Kerala State, India. 2006:104.
Begum 2002 {published data only}
-
- Begum A. Loading dose vs standard regime of magnesium sulphate in the management of eclampsia ‐ a randomized trial. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology (Book 2); 2000 Sept 3‐8; Washington DC, USA. 2000:47.
-
- Begum MR, Begum A, Quadir E. Loading dose versus standard regime of magnesium sulfate in the management of eclampsia: a randomized trial. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2002;28:154‐9. - PubMed
Begum 2009 {published data only}
-
- Begum K. A lower dose of magnesium sulphate for control of convulsion in eclamptic women of Bangladesh. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S124.
China 2000 {published data only}
-
- Dianrong S, Lirong Y, Yinglin L. A comparison of phentolamine and magnesium sulphate in pre‐eclampsia. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2000;68:259‐60. - PubMed
Chissell 1994 {published data only}
-
- Chissell S, Botha JH, Moodley J, McFadyen L. Intravenous and intramuscular magnesium sulphate regimens in severe pre‐eclampsia. South African Medical Journal 1994;84:607‐10. - PubMed
Chowdhury 2009 {published data only}
-
- Chowdhury JR, Chaudhuri S, Bhattacharyya N, Biswas PK, Panpalia M. Comparison of intramuscular magnesium sulfate with low dose intravenous magnesium sulfate regimen for treatment of eclampsia. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2009;35(1):119‐25. - PubMed
Ehrenberg 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ehrenberg H, Mercer B. Abbreviated post‐partum magnesium sulfate therapy for women with mild preeclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2004;191(6 Suppl 1):S73. - PubMed
-
- Ehrenberg HM, Mercer BM. Abbreviated postpartum magnesium sulfate therapy for women with mild preeclampsia: a randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2006;108(4):833‐8. - PubMed
Fontenot 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fontenot MT, Lewis DF, Frederick JB, Wang Y, DeFranco EA, Groome LJ, et al. A prospective randomized trial of magnesium sulfate in severe preeclampsia: use of diuresis as a clinical parameter to determine the duration of postpartum therapy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2005;192:1788‐94. - PubMed
Ghahiri 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ghahiri A, Berjis K. A comparison between intravenous magnesium sulfate and oral magnesium chloride in mild preeclampsia. Journal of Research in Medical Sciences 2005;10(1):6‐9.
Hangarga 2001 {published data only}
-
- Hangarga US, Pragya S. A comparative study of phenytoin sodium with magnesium sulphate and Menon's regime in the treatment of eclampsia. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India 2001;51(3):68‐70.
Laiteerapong 1999 {published data only}
-
- Laiteerapong U, Leelahakorn S. Comparative study of serum magnesium levels attained from magnesium sulfate therapy for severe pre‐eclamptic patients between 1 gm/hr and 2 gm/hr regimen. Thai Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1999;11(4):281.
Li 1998 {published data only}
-
- Li M, Yang M, Qiu X. The effect of nimodipine on retinal blood flow in pregnancy induced hypertension. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zh 1998; Vol. 33, issue 7:397‐9. - PubMed
Maheshwari 1989 {published data only}
-
- Maheshwari JR, Desai SV, Hansotia MD, Walvekar VR. Anti‐convulsant therapy in eclampsia. Journal of Postgraduate Medicine 1989;35(2):66‐9. - PubMed
Muhammad 2009 {published data only}
-
- Muhammad A, Ibrahim U, Nighat K, Muhammad Y, Abdullahi A. Low dose magnesium sulfate in the control of eclamptic fits: a randomized control trial. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S277‐8.
Mundle 2009 {published data only}
-
- Mundle S, Regi A, Biswas B, Bracken H, Easterling T, Winikoff B. Preeclampsia in low‐resource settings: a randomized trial of IV MgSO4 via flow controlled pump. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2009;107(Suppl 2):S278.
Nagar 1988 {published data only}
-
- Nagar S, Jain S, Kumari S, Ahuja L. Reassessment of therapy of eclampsia: comparison of mortality and morbidity of mother and fetus with parenteral magnesium sulphate and lytic cocktail therapy. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of India 1988;38(3):250‐5.
Neto 2000 {published data only}
-
- Neto JDV, Bertini AM, Taborda WC, Parente JV. Treatment of eclampsia: comparative study on the use of magnesium sulfate and phenytoin [Tratamento da eclampsia:estudio comparativo entre sulfato de magnesio e a fenitoina]. Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetricia 2000;22(9):543‐9.
Ola 2004 {published data only}
-
- Ola RE, Odeneye OT, Abudu OO. Eclampsia: a randomized double blind trial of magnesium sulphate and diazepam in Lagos, Nigeria. Tropical Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2004;21(2):143‐7.
Rodriquez 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rodriquez Cruz CM, Suero Holguin HJ, Pena Acosta CA, Cots Martinez JM, Garcia CA, Camilo MA. Magnesium sulfate versus diazepam in the treatment of severe preeclampsia [Sulfato de magnesio versus diazepam en el manejo de la pre‐eclampsia severa]. Acta Medica Dominicana 1990;12(5):171‐5.
Rudnicki 1990 {published data only}
-
- Rudnicki M, Junge J, Frolich A, Ornvold K, Fischer‐Rasmussen W. Magnesium supplement in pregnancy‐induced hypertension. A clinicopathological study. APMIS 1990;98:1123‐7. - PubMed
Rudnicki 1991 {published data only}
-
- Rudnicki M, Frolich A, Rasmussen WF, McNair P. The effect of magnesium on maternal blood pressure in pregnancy‐induced hypertension. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 1991;70:445‐50. - PubMed
Samal 2001 {published data only}
-
- Samal S, Gupta U, Agarwal P. Management of eclampsia with magnesium sulphate and nifedipine. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India 2001;51(3):71‐4.
Shilva 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shilva, Saha SC, Kalra J, Prasad R. Safety and efficacy of low‐dose MgSO4 in the treatment of eclampsia. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2007;97(2):150‐1. - PubMed
Smith 2005 {published data only}
-
- Smith D, Warren J, Saade G, Clark S, Belfort M. Oral labetalol given to treated non hypertensive patients with preeclampsia is no more likely to cause hypotension than magnesium sulfate [abstract]. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2005;193(6 Suppl):S78.
South Africa 1996 {published data only}
-
- Payne AJ, Naidu S, Moodley J, Hoffmann M, Gouws F. Non‐invasive assessment of the maternal cerebral circulation by transcranial doppler ultrasound in the hypertensive crises of pregnancy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1996;174:320.
Suneja 2008 {published data only}
-
- Suneja A, Sinha S, Vaid N, Ahuja S. A prospective randomized controlled trial to individualize the duration of post partum magnesium sulfate therapy. Hypertension in Pregnancy 2008;27(4):504.
Tanzania 1994 {published data only}
-
- Ramsay M, Rimoy G, Rubin P. Are anticonvulsants necessary to prevent eclampsia?. Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of the International Society for the Study of Hypertension in Pregnancy; 1994 March 15‐18; Sydney, Australia. 1994:279.
-
- Ramsay MM, Rimoy GH, Rubin PC. Are anticonvulsants necessary to prevent eclampsia. Lancet 1994;343:540‐1. - PubMed
Tongsong 1992 {published data only}
-
- Tongsong T, Dejkijwikrom W, Tansuwannont W, Jantachai U, Siangpura U. A comparison of intravenous magnesium sulfate regimens in preeclampsia‐eclampsia between rate 1 gram and 2 grams per hour. Siriraj Hospital Gazette 1992;44(7):509‐16.
UK 1989 {published data only}
-
- Slater RM, Wilcox FL, Smith WD, Maresh M. Phenytoin in pre‐eclampsia. Lancet 1989;ii:1224‐5. - PubMed
USA ‐ Texas 1991 {published data only}
-
- Appleton M, Kuehl T, Raebel M, Adams H, Pickens J, Koops B, et al. Magnesium sulfate vs. phenytoin in pregnancy‐induced hypertension. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1991;164:273. - PubMed
-
- Appleton MP, Kuehl TJ, Raebel MA, Adams HR, Knight AB, Gold WR. Magnesium sulfate versus phenytoin for seizure prophylaxis in pregnancy‐induced hypertension. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1991;165:907‐13. - PubMed
USA ‐ Texas 1992 {published data only}
-
- Belfort MA, Moise KJ. Effect of magnesium sulfate on maternal brain blood flow in preeclampsia: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1992;167:661‐6. - PubMed
-
- Belfort MA, Moise KJ, Saade G. The effect of magnesium sulfate on maternal retinal blood flow in pregnancy‐induced hypertension: a randomized placebo‐controlled study. Proceedings of 39th Annual Meeting of the Society for Gynecologic Investigation; 1992 March 18‐21; San Antonio, USA. 1992:233.
-
- Belfort MA, Saade GR, Moise KJ. The effect of magnesium sulfate on maternal retinal blood flow in preeclampsia: a randomized placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1992;167:1548‐53. - PubMed
Varma 1972 {published data only}
-
- Varma T. Chlormethiazole in the treatment of pre‐eclampsia. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of the British Commonwealth 1972;79:513‐7. - PubMed
Wang 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wang Y, Philibert L, Zhang Y, Gu Y, Tynes K, Lewis DF. Effects of magnesium sulfate on prostacyclin and thromboxane in women with severe preeclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;189(6 Suppl 1):S92.
References to ongoing studies
USA ‐ Utah {published data only}
-
- Belfort MA. Labetalol versus MgSO4 for the prevention of eclampsia trial (ongoing trial). ClinicalTrials.gov (http://clinicaltrials.gov/) (accessed 21 March 2006).
-
- Warren J, Lacoursiere Y, Varner M, Silver R, Anthony J, Belfort M. First interim report on the labetalol versus magnesium sulfate for the prevention of eclampsia trial (LAMPET). Hypertension in Pregnancy 2004;23(Suppl 1):9.
Additional references
Abalos 2007
Begum 2001
-
- Begum R, Begum A, Johanson R, Ali MN, Akhter S. A low dose ("Dhaka") magnesium sulphate regime for eclampsia. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica 2001;80(11):998‐1002. - PubMed
Belfort 1992
-
- Belfort MA, Moise KJ. Effect of magnesium sulfate on maternal brain blood flow in preeclampsia: a randomized, placebo‐controlled study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1992;167(3):661‐6. [PUBMED: 1530019] - PubMed
Churchill 2002
Collab Trial 1995
-
- The Eclampsia Trial Collaborative Group. Which anticonvulsant for women with eclampsia? Evidence from the Collaborative Eclampsia Trial. Lancet 1995;345:1455‐63. - PubMed
Crowther 2003
Douglas 1994
Doyle 2009
Duley 1992
-
- Duley L. Maternal mortality associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in Africa, Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1992;99:547‐53. - PubMed
Duley 1994
-
- Duley L, Johanson R. Magnesium sulphate for pre‐eclampsia and eclampsia: the evidence so far. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1994;101:565‐7. - PubMed
Duley 1996
-
- Duley L. Magnesium sulphate regimens for women with eclampsia: messages from the Collaborative Eclampsia Trial. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1996;103(2):103‐5. - PubMed
Duley 1999
Duley 2000
Duley 2003a
Duley 2003b
Duley 2006
Duley 2008
Duley 2009
-
- Duley L, Henderson‐Smart DJ, Walker GJA. Interventions for treating pre‐eclampsia and its consequences: generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007756] - DOI
Euser 2009
Goldman 1988
-
- Goldman RS, Finkbeiner SM. Therapeutic use of magnesium sulfate in selected cases of cerebral ischemia and seizure. New England Journal of Medicine 1988; Vol. 319, issue 18:1224‐5. [PUBMED: 3173462] - PubMed
Gülmezoglu 1998
Higgins 2009
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Jones 2002
Langer 2008
-
- Langer A, Villar J, Tell K, Kim T, Kennedy S. Reducing eclampsia‐related deaths‐‐a call to action. Lancet 2008;371(9614):705‐6. - PubMed
Magpie 2004
-
- Magpie Trial Follow Up Study Management Group, Magpie Trial Follow Up Study Collaborative Group. The Magpie Trial follow up study: outcome after discharge from hospital for women and children recruited to a trial comparing magnesium sulphate with placebo for pre‐eclampsia. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2004;4:5. - PMC - PubMed
Mittendorf 1998
-
- Mittendorf R, Covert R, Boman J, Khoshnood B, Kwang‐Sun L, Siegler M. Is tocolytic magnesium sulphate associated with increased total paediatric mortality?. Lancet 1997;350:1517‐8. - PubMed
Nelson 1995
-
- Nelson KB, Grether JK. Can magnesium sulfate reduce the risk of cerebral palsy in very low birthweight infants?. Pediatrics 1995;95:263‐9. - PubMed
North 2009
-
- North RA, Taylor RN. Subclinical hypothyroidism after pre‐eclampsia. BMJ 2009;339:b5183. - PubMed
Pritchard 1955
-
- Pritchard JA. The use of the magnesium ion in the management of eclamptogenic toxemias. Surgery, Gynecology and Obstetrics 1955;100(2):131‐40. - PubMed
Pritchard 1984
-
- Pritchard JA, Cunningham FG, Pritchard SA. The Parkland Memorial Hospital protocol for treatment of eclampsia: evaluation of 245 cases. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1984;148(7):951‐63. - PubMed
RCOG 2006
-
- Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. RCOG Green‐top Guidelines. The Management of Severe Pre‐Eclampsia/Eclampsia. London: RCOG, 2006.
RevMan 2008 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.0. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008.
Sadeh 1989
-
- Sadeh M. Action of magnesium sulfate in the treatment of preeclampsia‐eclampsia. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 1989;20(9):1273‐5. [PUBMED: 2672428] - PubMed
Scudiero 2000
-
- Scudiero R, Khoshnood B, Pryde PG, Lee KS, Wall S. Perinatal death and tocolytic magnesium sulfate. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2000;96:178‐82. - PubMed
Sheth 2002
-
- Sheth SS, Chalmers I. Magnesium for preventing and treating eclampsia: time for international action. Lancet 2002;359(9321):1872‐3. - PubMed
Sibai 1990
-
- Sibai BM. Magnesium sulfate is the ideal anticonvulsant in preeclampsia‐eclampsia. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1990;162(5):1141‐5. - PubMed
Simon 2006
-
- Simon J, Gray A, Duley L, on behalf of the Magpie Trial Collaborative Group. Cost‐effectiveness of prophylactic magnesium sulphate for 9996 women with pre‐eclampsia from 33 countries: economic evaluation of the Magpie Trial. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2006;113(2):144‐51. - PubMed
Squires 1999
-
- Squires J, Potter L, Bricker D. The ASQ user's guide for the Ages and Stages Questionnaires: a parent completed, child monitoring system. 2nd Edition. Baltimore: Paul Brookes Publishing Co, 1999.
Vargas 1998
-
- Vargas AG, Salmeron PI, Sanchez GAR, Jiminez AL, Rubio GAF. Efficancy of isosorbide in aerosol in the management of hypertensive crisis of severe preeclampsia [Eficacia del isosorbide en aerosol en el manejo de la crisis hipertensiva de la preeclampsia]. Ginecologia y Obstetricia De Mexico 1998;66:316‐9. - PubMed
Walss 1992
-
- Walss Rodriguez RJ, Levario AR. Anticonvulsant treatment of severe pre‐eclampsia: comparison of diazepam and magnesium sulfate. Ginecologia y Obstetricia de Mexico 1992;60:331‐5. - PubMed
WHO 1988
-
- World Health Organization International Collaborative Study of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Geographic variation in the incidence of hypertension in pregnancy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1988;158:80‐3. - PubMed
Zuspan 1978
-
- Zuspan FP. Problems encountered in the treatment of pregnancy‐induced hypertension. A point of view. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1978;131(6):591‐7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

