Synthesis and identification of new 4-arylidene curcumin analogues as potential anticancer agents targeting nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 21070043
- PMCID: PMC3990230
- DOI: 10.1021/jm1004545
Synthesis and identification of new 4-arylidene curcumin analogues as potential anticancer agents targeting nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
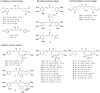
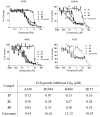
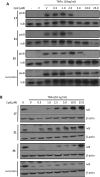
A series of curcumin analogues including new 4-arylidene curcumin analogues (4-arylidene-1,7-bisarylhepta-1,6-diene-3,5-diones) were synthesized. Cell growth inhibition assays revealed that most 4-arylidene curcumin analogues can effectively decrease the growth of a panel of lung cancer cells at submicromolar and low micromolar concentrations. High content analysis technology coupled with biochemical studies showed that this new class of 4-arylidene curcumin analogues exhibits significantly improved NF-κB inhibition activity over the parent compound curcumin, at least in part by inhibiting IκB phosphorylation and degradation via IKK blockage; selected 4-arylidene curcumin analogues also reduced the tumorigenic potential of cancer cells in a clonogenic assay.
Figures


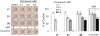


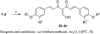
References
-
- Ghosh S, May M, Kopp E. NF-κB and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Hayden M, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. The two NF-κB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2004;25:280–288. - PubMed
-
- Ni H, Ergin M, Huang Q, Qin J, Amin H, Martinez R, Saeed S, Barton K, Alkan S. Analysis of expression of nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) in multiple myeloma: downregulation of NF-κB induces apoptosis. Br J Haematol. 2001;115:279–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

