Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice
- PMID: 21070404
- PMCID: PMC2996852
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04324.x
Two LysM receptor molecules, CEBiP and OsCERK1, cooperatively regulate chitin elicitor signaling in rice
Abstract
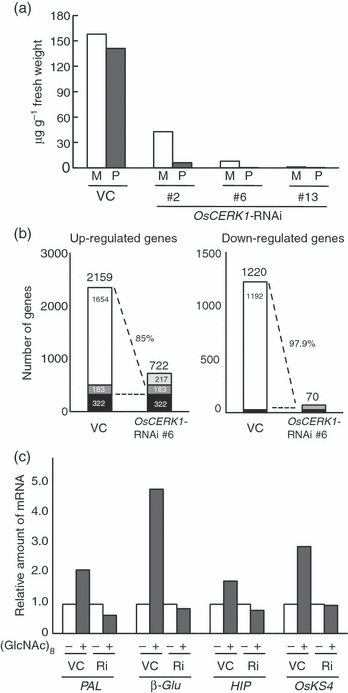
Chitin is a major molecular pattern for various fungi, and its fragments, chitin oligosaccharides, are known to induce various defense responses in plant cells. A plasma membrane glycoprotein, CEBiP (chitin elicitor binding protein) and a receptor kinase, CERK1 (chitin elicitor receptor kinase) (also known as LysM-RLK1), were identified as critical components for chitin signaling in rice and Arabidopsis, respectively. However, it is not known whether each plant species requires both of these two types of molecules for chitin signaling, nor the relationships between these molecules in membrane signaling. We report here that rice cells require a LysM receptor-like kinase, OsCERK1, in addition to CEBiP, for chitin signaling. Knockdown of OsCERK1 resulted in marked suppression of the defense responses induced by chitin oligosaccharides, indicating that OsCERK1 is essential for chitin signaling in rice. The results of a yeast two-hybrid assay indicated that both CEBiP and OsCERK1 have the potential to form hetero- or homo-oligomers. Immunoprecipitation using a membrane preparation from rice cells treated with chitin oligosaccharides suggested the ligand-induced formation of a receptor complex containing both CEBiP and OsCERK1. Blue native PAGE and chemical cross-linking experiments also suggested that a major portion of CEBiP exists as homo-oligomers even in the absence of chitin oligosaccharides.
© 2010 The Authors. Journal compilation © 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
OsCERK1 and OsRLCK176 play important roles in peptidoglycan and chitin signaling in rice innate immunity.Plant J. 2014 Dec;80(6):1072-84. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12710. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 25335639
-
Functional characterization of CEBiP and CERK1 homologs in arabidopsis and rice reveals the presence of different chitin receptor systems in plants.Plant Cell Physiol. 2012 Oct;53(10):1696-706. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcs113. Epub 2012 Aug 13. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22891159
-
Chitin-induced activation of immune signaling by the rice receptor CEBiP relies on a unique sandwich-type dimerization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 21;111(3):E404-13. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1312099111. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24395781 Free PMC article.
-
Defense Against Pathogens: Structural Insights into the Mechanism of Chitin Induced Activation of Innate Immunity.Curr Med Chem. 2017 Nov 24;24(36):3980-3986. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161221124345. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28003004 Review.
-
Plant immunity and symbiosis signaling mediated by LysM receptors.Innate Immun. 2018 Feb;24(2):92-100. doi: 10.1177/1753425917738885. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Innate Immun. 2018. PMID: 29105533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of LysM receptors in chitin-triggered plant innate immunity.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Jan;8(1):e22598. doi: 10.4161/psb.22598. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23221760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome Profiling of Buffalograss Challenged with the Leaf Spot Pathogen Curvularia inaequalis.Front Plant Sci. 2016 May 25;7:715. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00715. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27252728 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Fungal Elicitor-Triggered Plant Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 9;23(19):12003. doi: 10.3390/ijms231912003. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross Kingdom Immunity: The Role of Immune Receptors and Downstream Signaling in Animal and Plant Cell Death.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 8;11:612452. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.612452. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33763054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cotton Wall-Associated Kinase GhWAK7A Mediates Responses to Fungal Wilt Pathogens by Complexing with the Chitin Sensory Receptors.Plant Cell. 2020 Dec;32(12):3978-4001. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00950. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 33037150 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinchilla D, Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Kemmerling B, Nurnberger T, Jones JD, Felix G, Boller T. A flagellin-induced complex of the receptor FLS2 and BAK1 initiates plant defence. Nature. 2007;448:497–500. - PubMed
-
- Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ. Host–microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell. 2006;124:803–814. - PubMed
-
- Desaki Y, Miya A, Venkatesh B, Tsuyumu S, Yamane H, Kaku H, Minami E, Shibuya N. Bacterial lipopolysaccharides induce defense responses associated with programmed cell death in rice cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006;47:1530–1540. - PubMed
-
- Gimenez-Ibanez S, Hann DR, Ntoukakis V, Petutschnig E, Lipka V, Rathjen JP. AvrPtoB targets the LysM receptor kinase CERK1 to promote bacterial virulence on plants. Curr. Biol. 2009;19:423–429. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

